Alcohol Use Disorder (Alcohol Addiction) Definition, Cycle, Signs, Treatment
Alcohol addiction, also known as alcoholism, is a chronic disease where individuals lose control over their drinking habits despite harmful consequences. Alcohol use disorder is marked by both physical and psychological dependence, which causes significant damage to one’s health and life over time. According to the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) released by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) in November 2023, 29.5 million Americans aged 12 or older had an alcohol use disorder in the past year.

Alcohol addiction, also known as alcoholism, is a chronic disease where individuals lose control over their drinking habits despite harmful consequences. Alcohol use disorder is marked by both physical and psychological dependence, which causes significant damage to one’s health and life over time. According to the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) released by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) in November 2023, 29.5 million Americans aged 12 or older had an alcohol use disorder in the past year.
The cycle of alcohol addiction is divided into three distinct phases. The binge/intoxication stage involves excessive drinking and experiencing pleasure from alcohol. In the negative affect/withdrawal stage, individuals face emotional distress, irritability, or depression when not drinking. The final phase, the preoccupation/anticipation stage, is characterized by intense cravings and obsessive thinking about alcohol.
The signs of alcohol addiction include a strong craving or compulsion to drink, an inability to limit alcohol intake, and experiencing withdrawal symptoms like nausea, tremors, or anxiety when alcohol is not consumed. These signs indicate a dependency that worsens without treatment.
The types of treatment options for alcohol addiction include behavioral therapies, medication, and support groups. Behavioral therapies, like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), help individuals address underlying emotional triggers. Medications such as naltrexone or acamprosate reduce cravings or block the pleasurable effects of alcohol. Support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) provide peer-based assistance and long-term recovery support.
What is the Cycle of Alcohol Addiction?
The cycle of alcohol addiction is a repeated pattern of alcohol use that progresses through 3 stages (binge/intoxication stage, withdrawal/negative affect stage, and preoccupation/anticipation stage), leading to physical and psychological dependence. The cycle of alcohol addiction includes 6 phases, each leading to deeper dependence on alcohol. The process begins with initial use, where an individual first consumes alcohol, in social settings or due to curiosity or life circumstances. As alcohol use continues, abuse follows, where drinking becomes a recurring response to stress, anxiety, or the desire for a euphoric effect. This stage marks the development of unhealthy drinking patterns.
Tolerance develops when the body requires increasingly larger amounts of alcohol to achieve the same effect. This increased tolerance then progresses into dependence, where the body relies on alcohol to function normally, and withdrawal symptoms like irritability, anxiety, and nausea occur in the absence of alcohol.
Addiction emerges when alcohol becomes the central focus of the individual’s life, leading to compulsive drinking despite the severe negative impact on health, relationships, and responsibilities. Attempts to quit lead to relapse, where withdrawal symptoms, cravings, or emotional triggers push the individual back into alcohol use.
This addiciton cycle is further broken into three main stages including the binge/intoxication stage, withdrawal/negative affect stage, and preoccupation/anticipation stage. The cycle of alcohol addiction repeats itself, leading individuals through these stages over weeks, months, or even several times in a single day. It is a widespread issue affecting millions. It is estimated that 5.1% of the global burden of disease and injury was attributable to alcohol consumption according to The World Health Organization (WHO) Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018. Proper support and treatment are needed to break the cycle, restoring health and preventing further harm.
How Does Addiction Develop in the Brain?
Addiction develops in the brain by altering the brain’s pleasure circuits, which causes alcohol to trigger dopamine release, creating feelings of euphoria and relaxation. Over time, the brain becomes dependent on alcohol to release dopamine, driving compulsive drinking behavior. These brain changes, along with the discomfort of withdrawal, make it challenging for individuals with AUD to change their habits, according to a study by The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism titled “Neuroscience: The Brain in Addiction and Recovery.”
Alcohol has both short- term effects on the brain. In the short term, it impairs judgment, coordination, speech, and memory. Long-term effects include cognitive decline, memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and emotional instability, potentially leading to conditions like dementia or mood disorders. While brain damage from alcohol addiction can be permanent according to the NIAAA, recovery is possible with early intervention, long-term abstinence, and rehabilitation, though the extent depends on factors like age and addiction duration.
What are the Stages of the Addiction Cycle?
The stages of the addiction cycle are the Binge/Intoxication Stage, the Negative Affect/Withdrawal Stage, and the Preoccupation/Anticipation Stage. Alcohol addiction is a spectrum disorder that ranges from mild to severe and includes alcohol abuse, alcohol dependence, or alcoholism. Alcohol addiction represents the moderate to severe range of the AUD spectrum according to research titled “The Cycle of Alcohol Addiction” published by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
The 3 stages of the addiction cycle include:
-
Binge/Intoxication Stage: During the Binge/Intoxication Stage, alcohol consumption activates the brain's reward system, particularly in the basal ganglia, which produces feelings of euphoria, reduces anxiety, and eases social interactions. This repeated activation reinforces alcohol consumption, forming habits and associating alcohol with specific cues like certain people or environments. Over time, these stimuli trigger cravings, leading to compulsive drinking.
-
Negative Affect/Withdrawal Stage: In the Negative Affect/Withdrawal Stage, individuals experience both physical and emotional withdrawal symptoms, such as anxiety, irritability, and dysphoria, when they stop drinking. The brain's reward system is less responsive, making it difficult to find pleasure in everyday activities. At the same time, the brain’s stress systems become overactive, amplifying feelings of unease. Instead of drinking for pleasure, individuals in this stage drink to avoid the negative effects of withdrawal.
-
Preoccupation/Anticipation Stage: In the Preoccupation/Anticipation Stage, individuals become obsessed with alcohol and plan for their next drink after a period of abstinence. Impairment in the prefrontal cortex, which governs executive functions like decision-making and impulse control, fuels this stage. As a result, cravings intensify, making it difficult for the individual to resist drinking, further perpetuating the addiction cycle.
What Are the Signs, Symptoms, and Causes of Alcohol Use Disorder?
The signs, symptoms and causes of Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) are increased tolerance to alcohol, withdrawal symptoms, loss of control, neglecting responsibilities, social or interpersonal problems, engaging in risky behaviors, experiencing alcohol cravings, spending excessive time drinking, genetic predisposition, environmental influences, psychological factors, social pressures, cultural influences, and the impact of stress and trauma. It is necessary to understand the physical and emotional symptoms, behavioral signs and underlying causes of alcohol use disorder in order to find or provide proper treatment for alcohol addiction.
Symptoms of Alcohol Use Disorder

The symptoms of alcohol use disorder include physical and emotional changes like increased tolerance, physical withdrawal symptoms and uncontrollable cravings. The symptoms of alcohol use disorder are given below:
-
Increased Tolerance to Alcohol: Tolerance occurs when a person needs more alcohol to achieve the same effects. Over time, this becomes a moderate to severe symptom of AUD, as the brain adapts to alcohol, leading to higher consumption. For example, someone who once felt relaxed after one drink now needs multiple drinks to experience the same feeling. Every person is able to raise their alcohol tolerance until it reaches a trigger point where he or she needs alcohol to feel normal according to a study titled “The truth about tolerance” written by Hahn, A. 2016 and published by University of Health Services UW Madison.
-
Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms: Withdrawal symptoms occur when a person stops drinking, including physical symptoms like shaking or nausea and emotional symptoms like anxiety or irritability. This is a severe symptom because it indicates physical dependence on alcohol. For example, a person experiences tremors in the morning or feels intense anxiety without drinking. Alcohol withdrawal seizures are a severe manifestation of alcohol withdrawal syndrome, typically occurring 6 to 48 hours after alcohol cessation as blood alcohol levels approach zero. These seizures are caused by the sudden reduction in alcohol intake after prolonged, heavy use according to a study by Schacht, J. P., & Randall, P. K. 2023. in “Alcohol withdrawal,” published by StatPearls.
-
Alcohol Cravings: Cravings are the intense desire to drink alcohol and are felt when not drinking. These cravings can range from moderate to severe, depending on how frequently cravings occur. For instance, someone feels a constant urge to drink during stressful times or even during relaxation after a long day. According to Ruby Mehta in “Alcohol Cravings: Why They Happen and How to Manage Them.” published by Healthline, alcohol cravings are very intense, especially in early recovery. The good news is, cravings only last for a short period of time
Signs of Alcohol Use Disorder

The signs of alcohol use disorder include behavioral changes (loss of control, neglecting responsibilities, social problems, risky behavior, and excessive time spent drinking and thinking about alcohol). The signs of alcohol use disorder are given below:
-
Loss of Control: Loss of control refers to the inability to limit or stop drinking, even when one intends to. This is a significant sign of AUD because it shows compulsive behavior. For example, someone plans to have one drink but ends up binge drinking, or repeatedly fails at attempts to quit. Another example would be someone who drinks so much that they black out and don’t remember a significant portion of their experiences.
-
Neglecting Responsibilities because of Alcohol: This sign is evident when drinking interferes with a person’s ability to fulfill work, family, or personal obligations. It ranges from moderate to severe, depending on the impact on daily life. For instance, missing work due to a hangover or neglecting household duties because of drinking are common examples.
-
Social or Interpersonal Problems because of Alcohol: Alcohol use causes conflict with loved ones, marking this as a severe sign. Relationship strain, frequent arguments, or losing friendships due to alcohol are clear indicators. For example, frequent arguments with a spouse about drinking habits or losing friends over irresponsible behavior are typical scenarios.
-
Risky Behaviors caused by Alcohol: Risky behaviors, such as driving while intoxicated or engaging in unsafe sexual practices, are a severe sign of AUD. These behaviors show impaired judgment and lead to dangerous consequences. For instance, drunk driving poses life-threatening risks, while unprotected sexual encounters increase health risks.
-
Time Spent Drinking: Spending excessive time drinking or recovering from its effects is a serious sign of AUD. This behavior indicates that alcohol dominates a person’s daily routine. For example, someone might dedicate their weekends to drinking or require an entire day to recover from a hangover, impacting other responsibilities.
Causes of Alcohol Use Disorder
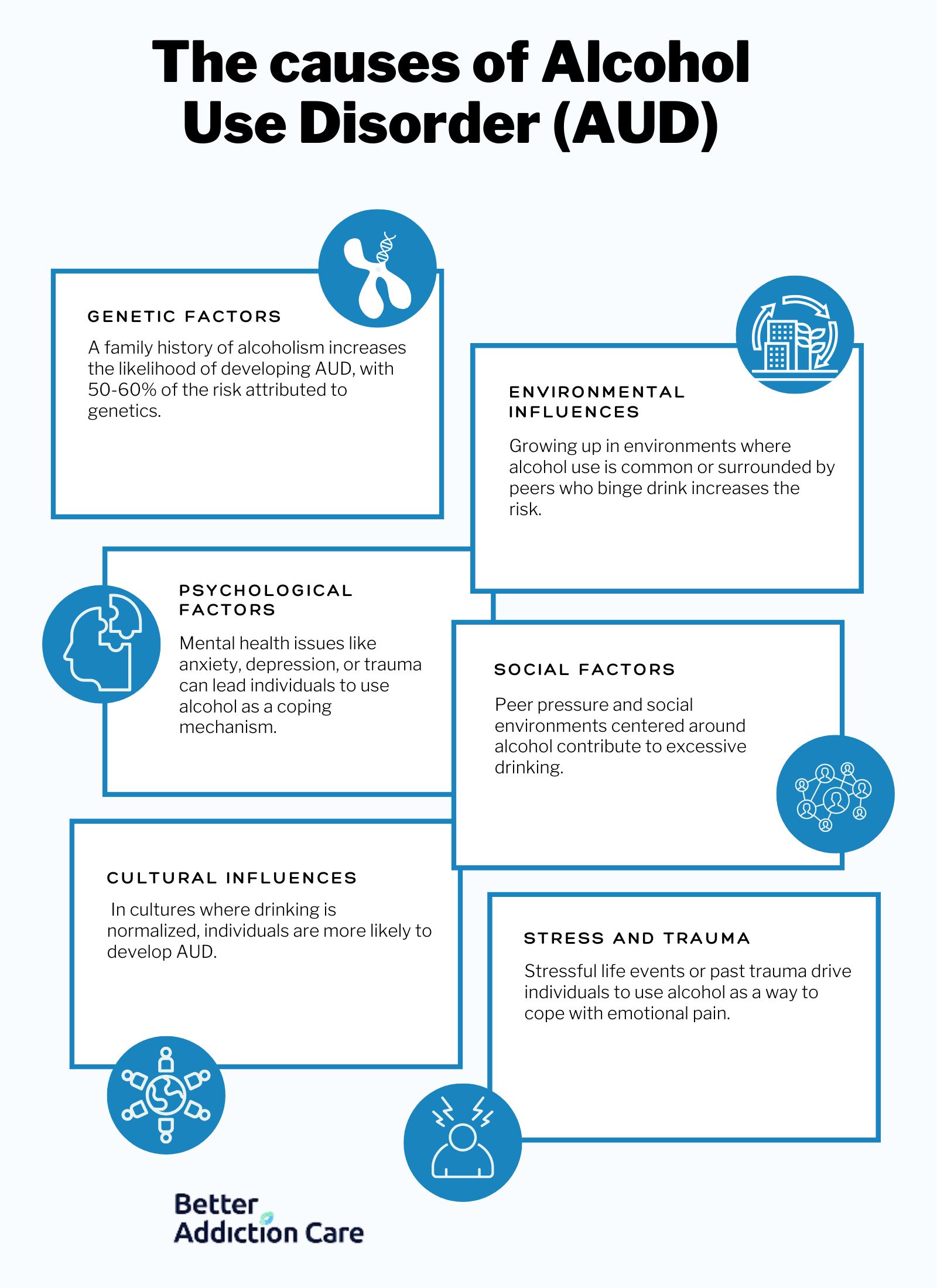
The causes of alcohol use disorder include genetic factors, environmental influences, psychological factors, social factors, cultural influences, stress and trauma. The causes of alcohol use disorder are given below:
-
Genetic Factors: Genetics are a factor in a person’s risk of developing AUD, making it a significant cause. People with a family history of alcohol dependence are more susceptible. For example, children of alcoholic parents inherit a higher likelihood of developing AUD, and genetic variations influence how alcohol is metabolized. About 50-60% of the risk of alcohol use disorder is attributable to genetic factors, as studied by Abel, T. in his book titled “Encyclopedia of Behavioral Neuroscience.”
-
Environmental Influences: The environment significantly affects drinking behaviors, making it a moderate cause. Growing up in a household where alcohol use is common or being part of social circles that promote heavy drinking increases the risk of AUD. For example, a college student surrounded by binge-drinking peers or living in a culture that normalizes alcohol use develops unhealthy drinking patterns.
-
Psychological Factors: Mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, or trauma contribute to the development of AUD. This is a moderate to severe cause, depending on the individual’s psychological state. For example, someone with depression uses alcohol as a coping mechanism, or an individual with anxiety turns to alcohol for temporary relief. According to SAMHSA's 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health, approximately 21.5 million adults in the United States have a co-occurring disorder for example depression and AUD.
-
Social Factors: Social pressure or relationships contribute to AUD, making it a moderate cause. Friends who drink heavily or social events centered around alcohol encourages overconsumption. For instance, peer pressure to drink at parties or constant invitations to alcohol-fueled gatherings push individuals to drink more than they should. Increased use of social media for alcohol marketing has paralleled changes in communication methods among adolescents and college-age youth according to Hoffman et al. 2014 and the Journal of American College Health.
-
Cultural Influences: Cultural norms surrounding alcohol consumption shape drinking behaviors, making this a primary cause. In cultures where drinking is deeply embedded in social practices, individuals are more likely to develop AUD. For example, in cultures where alcohol is part of celebrations or rites of passage, people consume alcohol more frequently. Many cultures use alcohol for social bonding, showing respect, and marking special occasions. For example, "cheersing" or toasting is common in the UK and other countries according to the American Psychological Association.
-
Stress and Trauma: Stressful life events or past trauma significantly contribute to AUD. Alcohol is used as a coping mechanism, making this a severe cause. For example, someone dealing with job loss or the death of a loved one turns to alcohol to numb their emotional pain, increasing their risk of addiction. 37% of people who misuse alcohol or had an alcohol dependence also had at least one serious mental health disorder according to the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) in a 2010 study titled “Mental Illness and Substance Abuse.”
What are the Types of Treatment for Alcohol Use Disorder?

The types of treatment for alcohol use disorder include medication, rehab, behavioral therapy, and support groups. Combining these 4 treatments allows for a comprehensive range of strategies to tackle the root causes of the addiction and provide coping mechanisms to prevent relapse. According to a study by Anton RF et al. (2008), titled “Naltrexone for the Management of Alcohol Dependence,” combining medication with therapy significantly improves treatment outcomes. The research found that individuals who used naltrexone alongside therapy were 25% more likely to maintain abstinence compared to those who did not incorporate both into their treatment plan.
The types of treatment for alcohol use disorder include:
-
Medications: There are several medications approved for treating alcohol use disorder, including naltrexone, acamprosate, and disulfiram. Naltrexone works by blocking the euphoria that alcohol provides, reducing cravings. Acamprosate helps to stabilize brain function after withdrawal, making it easier for individuals to maintain sobriety. Disulfiram causes unpleasant reactions when alcohol is consumed, discouraging use. Medications are used in conjunction with other forms of treatment for the best outcome.
-
Rehab Centers: Alcohol use disorder is treated in both inpatient and outpatient rehab centers. Inpatient centers provide 24/7 care in a structured environment, lasting 30 to 90 days. This option is ideal for individuals with severe addiction or co-occurring disorders. Outpatient programs allow individuals to live at home while attending treatment sessions several times a week. This is a good option for those with milder cases or strong external support systems.
-
Behavioral Treatments: Behavioral therapies treat alcohol use disorder by helping individuals change their drinking behavior. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is commonly used to help individuals identify and modify negative thought patterns related to alcohol. Motivational Enhancement Therapy (MET) helps individuals build motivation to change their drinking habits. Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) is used to manage emotional triggers that lead to alcohol use. These therapies are used to find the root causes and help individuals struggling with alcohol use disorder find coping strategies to avoid relapse.
-
Mutual-Support Groups: Mutual-support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), offer peer-led support for individuals in recovery. These groups provide a community of individuals with shared experiences, creating a support network that fosters accountability and encouragement. Many individuals continue to attend these meetings even after completing formal treatment as part of their aftercare plan to maintain long-term sobriety and prevent relapse.
What is the Withdrawal Timeline for Alcohol Addiction?

The withdrawal timeline for alcohol addiction starts within 6 to 12 hours after the last drink, peaks around 24 to 72 hours, and lasts from 5 to 10 days. Certain factors extend this timeline. For example, women experience more intense withdrawal symptoms due to faster alcohol absorption, while men, who drink more heavily, experience symptoms for a longer period. Heavy drinkers experience withdrawal symptoms lasting 7 to 10 days or even longer in severe cases according to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), .
Several factors influence how long withdrawal lasts including:
-
Heavy drinkers, defined as those consuming 15+ drinks per week for men or 8+ drinks per week for women. Individuals who drink heavily experience withdrawal lasting up to 10 days according to “Alcohol Withdrawal” published by the Cleveland Clinic.
. -
Delirium tremens (DTs), a severe withdrawal symptom, peaks around 48 to 72 hours after the last drink and is life-threatening without medical intervention. The lifetime risk for developing delirium tremens in the population with alcohol use disorder is approximately 5% to 10% according to “Delirium Tremens” from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
. -
A study by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) indicates that individuals undergoing detox with medical support experience symptoms for 2 to 8 days, with treatments helping to ease withdrawal symptoms and shorten withdrawal time.
Medically supervised detox programs help alleviate symptoms and reduce the duration of the withdrawal process, ensuring safety during severe withdrawal phases.
What Type of Healthcare Providers are used for Alcohol Use Disorder?
The types of healthcare providers used for alcohol use disorder offer unique expertise and services. According to “Types of Providers” published by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) it is a good idea to start with the doctor, nurse practitioner, or physician’s assistant that is your primary care provider (PCP)—this is the health care professional that you see regularly for your physical health. If you have anxiety, depression, or need help with quitting tobacco, healthcare providers will help.The different types of healthcare providers are detailed below:
-
Primary Care Provider (PCP): Primary care providers (PCPs) hold either a Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree. PCP’s are the first professionals individuals encounter when seeking help for alcohol use disorder. PCP’s diagnose the condition, prescribe medications such as naltrexone or disulfiram to reduce cravings and prevent relapse, and refer patients to specialists for further treatment. PCPs manage the overall physical health of individuals with alcohol use disorder, monitor the effects of alcohol on the body, and address co-occurring medical conditions that exacerbate addiction.
-
Psychiatrist (such as LMFT):Psychiatrists are medical doctors (MD or DO) who have specialized in psychiatry, with board certification by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN). Psychiatrists are uniquely qualified to address both the psychological and physiological components of alcohol use disorder. Psychiatrists diagnose mental health conditions that are contributing to alcohol use, such as depression or anxiety, and prescribe psychiatric medications alongside treatments for alcohol addiction, like acamprosate or anti-anxiety medications. Their role is imperative in managing co-occurring disorders and ensuring that both the mind and body are treated during recovery.
-
Psychologist (such as Ph.D., Psy.D., or Ed.D.): Psychologists hold a PhD or PsyD in psychology. Psychologists focus on behavioral treatments for alcohol use disorder. Psychologists cannot prescribe medications but are instrumental in offering therapies such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Motivational Interviewing (MI), and other psychotherapies that help individuals change their drinking behaviors and thought patterns. Psychologists work with patients to understand the underlying causes of their addiction, helping them develop coping strategies to prevent relapse and maintain long-term sobriety. Their role is to address the psychological aspects of addiction through evidence-based counseling.
-
Social Worker (such as LICSW, LCSW, or ACSW): Licensed Clinical Social Workers (LCSWs) hold a Master of Social Work (MSW) degree and are licensed by their state. Social workers provide support for individuals with alcohol use disorder. Social workers assist with counseling, helping patients manage the social, emotional, and family-related aspects of their addiction. Social workers also connect individuals with community resources, such as housing or employment services, that aid in their recovery. Social workers play a large role in coordinating care between different providers and ensuring that patients have access to the support they need outside of a clinical setting.
-
Counselor (such as LPC or LADC): Counselors hold a Master’s degree in counseling and certification as a Licensed Professional Counselor (LPC) or Certified Addiction Counselor (CAC). Counselors provide therapy to individuals dealing with alcohol addiction. Counselors use techniques like CBT and relapse prevention to guide patients through the recovery process. Counselors are involved in both one-on-one and group therapy sessions, focusing on emotional and psychological healing. Conselors play a role in helping individuals navigate the challenges of addiction recovery, offering support and strategies to maintain sobriety.
-
Alcohol Counselor: Alcohol counselors specialize in treating alcohol addiction and hold certifications like the Certified Alcohol and Drug Counselor (CADC). These professionals do not require advanced degrees, though some states require a Bachelor’s degree in addiction studies or a related field. Alcohol counselors focus specifically on guiding individuals through the recovery process by providing counseling, support, and practical strategies for overcoming alcohol dependence. Their role is to help individuals develop skills for avoiding triggers, managing stress, and maintaining sobriety in the long term.
-
Addiction Specialist: An addiction specialist is a medical doctor (MD or DO) who has completed additional certification in addiction medicine, typically from the American Board of Addiction Medicine (ABAM) or the American Board of Preventive Medicine (ABPM). Addiction specialists focus exclusively on treating substance use disorders, including alcohol addiction. Addiction specialists oversee medical detoxification, prescribe medications to manage withdrawal symptoms, and design long-term treatment plans tailored to each individual’s needs. Their role is to provide comprehensive medical care that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of addiction.
-
Nurse: Nurses, particularly those certified as Certified Addiction Registered Nurses (CARN), play an essential role in the treatment of alcohol use disorder. Nurses monitor patients during detoxification, administer medications to ease withdrawal symptoms, and provide ongoing medical care in both inpatient and outpatient settings. Nurses also offer education on managing withdrawal and alcohol dependence, supporting both the physical and emotional aspects of recovery. Their role is important in ensuring patient safety during detox and providing compassionate care throughout the recovery process.
How Does Alcohol Addiction Affect Health?
Alcohol addiction affects health in numerous ways including significantly harming both physical and mental health by damaging vital organs such as the liver, heart, and brain, leading to conditions like liver cirrhosis, heart disease, and cognitive decline. Alcohol addiction also weakens the immune system, increases the risk of several cancers, and contributes to mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression, further complicating recovery and overall well-being.
"Too much" drinking is defined by the amount of alcohol consumed over time. For men, heavy drinking is considered more than 15 drinks per week, and for women, it is more than 8 drinks per week. One standard drink typically contains about 14 grams of pure alcohol, equivalent to 12 ounces of beer (5% alcohol), 5 ounces of wine (12% alcohol), or 1.5 ounces of distilled spirits (40% alcohol). According to the CDC 25.1% of adults aged 18 and older who had at least one heavy drinking day (five or more drinks for men and four or more drinks for women) in the past year. Body weight significantly impacts how quickly alcohol is absorbed.
People with lower body weight experience the effects of alcohol more intensely and faster than those with higher body weight because women have less body mass to dilute the alcohol. According to the Mayo Clinic, women have higher blood alcohol concentrations (BAC) than men after consuming the same amount of alcohol, due to differences in body composition. Women have less water in their bodies, meaning alcohol is less diluted, which leads to faster absorption. Genetics, overall health, and metabolism also play significant roles in how alcohol affects individuals. For example, individuals with a family history of alcohol use disorder are more susceptible to developing addiction. People with underlying health conditions, such as liver disease or diabetes, are also at higher risk for severe alcohol-related complications.
How Does Alcohol Addiction Affect Your Social Life?
Alcohol addiction affects your social life by leading to strained relationships, unemployment, divorce, domestic abuse, and homelessness. Alcohol addiction impairs judgment and leads to job loss due to absenteeism or decreased productivity, causing financial instability. In personal relationships, alcohol exacerbates anger issues, resulting in increased domestic abuse, further damaging trust and family dynamics. Marital stress from alcohol addiction frequently leads to divorce. Additionally, the loss of employment and family support results in homelessness, as individuals struggle to maintain stable living conditions without a support system.
Why Do Alcoholics Drink?
Alcoholics drink because they are physically and psychologically dependent on alcohol. Alcohol is used to self-medicate underlying issues such as anxiety, depression, or trauma, providing temporary relief from emotional pain. Alcohol also alters brain chemistry, making it difficult for individuals to experience pleasure without drinking, leading to compulsive consumption. Lastly, social and environmental factors influence drinking behavior, as people drink to fit in, cope with stress, or deal with pressure from peers or life circumstances.
Can an Alcoholic Stop Drinking?
Yes, an alcoholic can stop drinking with the right support and treatment. Recovery is possible through a combination of medical detox, therapy, and ongoing support. Rehab centers offer structured programs that include medical supervision, counseling, and peer support to help individuals manage withdrawal symptoms, address underlying emotional issues, and develop healthier coping mechanisms for long-term sobriety.
What is Considered an Alcoholic?
To be considered an alcoholic, individuals typically engage in chronic, excessive drinking that leads to dependency and a loss of control over alcohol use. For men, this is generally defined as drinking more than 15 drinks per week, while for women, it is more than 8 drinks per week. These guidelines, outlined by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), help determine when alcohol use transitions into addiction. An alcoholic continues drinking despite facing serious personal, professional, or health-related consequences.
What Causes Alcohol Dependence?
The causes of alcohol dependence include three main factors including genetics, psychological and environmental influences. First, genetic predisposition plays a significant role, as individuals with a family history of alcohol use disorder are more likely to develop dependence themselves. Second, psychological factors, such as stress, anxiety, or depression, leads individuals to use alcohol as a coping mechanism, eventually leading to dependence. Third, environmental influences, including peer pressure, social norms, and access to alcohol, contributes to excessive drinking and the development of dependence over time.
Can You Get Addicted to Alcohol?
Yes, you can get addicted to alcohol. First, alcohol affects brain chemistry, causing the release of dopamine, which leads to feelings of pleasure and reinforces the behavior of drinking. Second, chronic alcohol use alters the brain’s reward system, making it difficult to feel pleasure without alcohol. Third, genetic factors increase the risk of addiction, as some people are more biologically susceptible to alcohol dependence due to their genetic makeup.
Can You Be Dependent on Alcohol?
Yes, you can be dependent on alcohol. First, physical dependence occurs when the body adapts to the constant presence of alcohol, resulting in withdrawal symptoms when alcohol is not consumed. Second, tolerance to alcohol builds over time, requiring more alcohol to achieve the same effects, which reinforces continued use. Third, psychological dependence to alcohol develops, where individuals feel they need alcohol to cope with stress or emotional issues, leading to compulsive drinking behavior.
Why Can’t I Stop Drinking?
You can't stop drinking because alcohol has created a physical and psychological dependence in your body. Prolonged drinking changes brain chemistry, making you crave alcohol and feel withdrawal symptoms when you try to quit. Social habits and emotional triggers reinforce your reliance on alcohol, making it difficult to quit without help.
Why Am I an Alcoholic?
You are an alcoholic due to a combination of biological factors, where your body has developed a dependency on alcohol, emotional reliance, using alcohol to deal with stress or difficult emotions, and environmental influences, such as being in situations that promote regular or heavy drinking. Together, these factors create an addiction that makes it difficult to control your drinking.
What Is a Chronic Alcoholic?
A chronic alcoholic is someone with a long-term, compulsive need to consume alcohol. This individual drinks excessively over extended periods, develops a high tolerance, and experiences withdrawal symptoms when not drinking. Despite severe personal, health, or social consequences, chronic alcoholics continue to drink, daily or in large amounts. According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Chronic conditions related to alcohol use include several types of cancer, heart disease, and liver disease including 53.7% of alcohol-related deaths are due to chronic misuse.
What Are the Pleasurable Effects of Alcohol?
Alcohol produces pleasurable effects by stimulating the release of dopamine in the brain. It reduces anxiety and stress while lowering inhibitions, making social interactions feel easier. These effects contribute to the temporary sensation of well-being, which leads to repeated use. Alcohol releases endorphins (the "pleasure hormones") which bind to opiate receptors in the brain, producing feelings of pleasure and reward according to “This is your brain on alcohol” published by Harvard Medical School.
Can People with Alcohol Use Disorder Recover?
Yes, people with alcohol use disorder can recover. Rehabs offer medical detox to manage withdrawal symptoms safely, making the initial step of recovery more manageable. Therapy and counseling in rehab centers help individuals address the underlying emotional and psychological causes of their addiction. Ongoing support through aftercare programs ensures long-term sobriety by providing tools and resources to prevent relapse. According to the Butler Center for Research at Hazelden Betty Ford Foundation about 89% of patients who complete alcohol rehab are still sober one month after discharge and 76% are still sober at 3 months
Why Are People Alcoholics?
People are alcoholics because of a combination of genetics, which increase the likelihood of addiction, high pressure life-styles, such as using alcohol to cope with trauma or emotional stress, and social environmental influences, like exposure to social drinking or peer pressure that encourages heavy alcohol use. Alcohol is also a widely used legal substance making it easy to access and well accepted in social settings. Worldwide, alcohol sales totaled more than $1.5 trillion in 2017 according to a study published in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
Is Alcohol Addictive?
Yes, alcohol is addictive for several reasons. First, it causes tolerance, meaning individuals need to consume more over time to achieve the same effects, leading to increased consumption. Second, it disrupts brain function, rewiring the brain's reward system to prioritize alcohol, making it harder to stop. Third, withdrawal symptoms like anxiety, tremors, and cravings make it difficult for individuals to quit drinking once dependence has formed, reinforcing the cycle of addiction.
What Is the Meaning of AUD?
AUD stands for Alcohol Use Disorder, a medical condition characterized by the inability to control alcohol consumption despite negative consequences. It ranges from mild to severe and involves a pattern of compulsive alcohol use, physical dependence, and cravings.
What Constitutes an Alcoholic?
An alcoholic is someone who suffers from alcohol dependence or addiction, marked by an inability to stop drinking despite harmful effects on their health, relationships, or responsibilities. An alcoholic experiences withdrawal symptoms when not drinking and develops a strong physical and psychological need for alcohol. According to the 2023 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) 28.9 million people ages 12 and older (10.2% of this age group) had Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) in the past year.
What Does Chronic Ethanol Mean?
Chronic ethanol is the long-term and excessive consumption of ethanol, which is the intoxicating component in alcoholic beverages. Chronic ethanol use leads to serious health problems such as liver damage, heart disease, and neurological issues due to the prolonged effects of alcohol on the body.




