Differences Between Being Drunk vs. Tipsy
The difference between being tipsy and drunk lies in the severity of cognitive functioning, coordination, and speech impairments, as well as variations in mood, inhibitions, memory lapses, and risk of harm.

The difference between being tipsy and drunk lies in the severity of cognitive functioning, coordination, and speech impairments, as well as variations in mood, inhibitions, memory lapses, and risk of harm.
Tipsiness is marked by slight impairments and increased sociability, whereas drunkenness results in significant impairments and emotional volatility, leading to a higher risk of harm.
According to Gowin, J. L.’s 2021 study, ‘Characteristics Associated With High-Intensity Binge Drinking in Alcohol Use Disorder’, raises the chances of traumatic injuries, suicidal behavior, cancer, and heart disease. Among 429 adults with alcohol use disorder, 41.5% engaged in high-intensity bingeing (12+ drinks for females, 15+ for males daily). These individuals spent 48% more time thinking about alcohol and had 4% higher depression rates. High-intensity bingeing is more common in rural areas and among nicotine or cannabis users.
What is Being Drunk?
Being drunk is a condition that occurs when you consume excessive alcohol, severely impairing your cognitive abilities and physical coordination. When intoxicated, a person's inhibitions decrease significantly, often leading to behaviors they wouldn't engage in while sober. The physical effects include difficulty walking steadily, slurred speech, and poor balance, while mental impairments lead to impulsive decision-making and reduced ability to cooperate with others. Increasing blood alcohol concentration results in dangerous consequences, including accidents, injuries, and potentially fatal alcohol poisoning. Drunk driving presents a serious hazard to both the impaired driver and innocent bystanders.
The prolonged effects of excessive alcohol consumption extend to addiction development, significant health deterioration, and various social problems. Regular heavy drinking damages vital organs, including the heart, liver, and brain. Frequent intoxication strains personal relationships, decreases performance at work or in academic settings, and results in legal consequences. Understanding alcohol's risks and recognizing the signs of excessive intoxication are essential steps toward responsible consumption and maintaining overall well-being.
What is Being Tipsy?
Being tipsy refers to a mild state of intoxication caused by alcohol consumption. When tipsy, individuals experience subtle changes in their physical and mental functioning. Their inhibitions slightly decrease, allowing them to be more outgoing without significantly disrupting others, even as they feel more relaxed and sociable. While minor coordination issues and slight speech slurring occur, most people remain functional. This state often brings feelings of happiness and increased confidence, enhancing social interactions. However, judgment remains somewhat impaired, requiring thoughtful decision-making to avoid potential problems.
This mild intoxication progresses to a more severe state if alcohol consumption continues. Additional drinking after becoming tipsy intensifies impairment and leads to drunkenness. To maintain a responsible level of intoxication, individuals should moderate their alcohol intake and understand their limits. Practicing responsible drinking enables enjoyable social experiences while minimizing the risks associated with excessive alcohol consumption.
How To Differentiate Being Drunk vs. Being Tipsy?
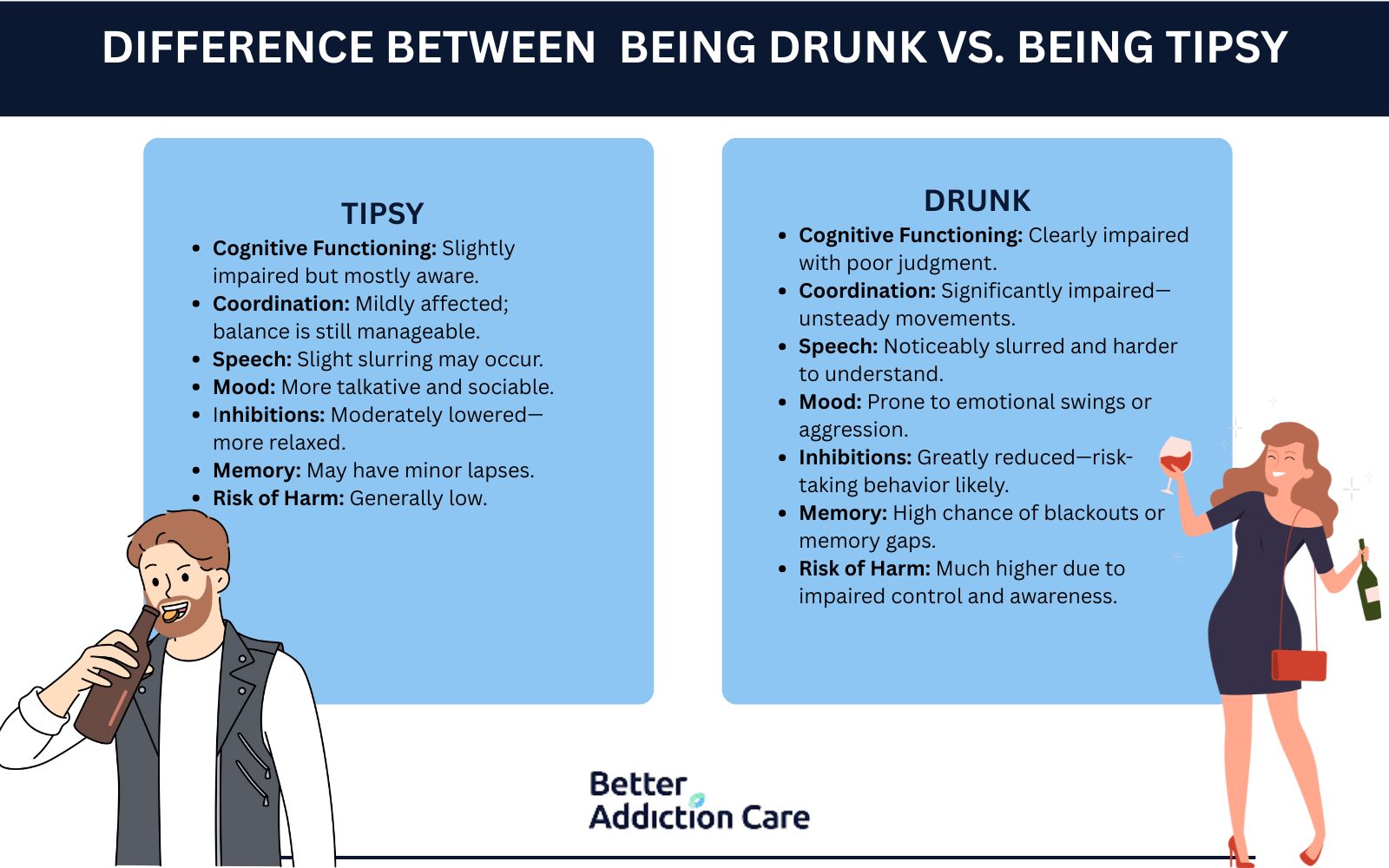
To differentiate between being drunk vs. being tipsy, look at factors like alcohol concentration in the body, mental clarity, physical coordination, speech clarity, emotional stability, and memory retention. Tipsy individuals experience mild effects with minimal impairment, while drunk persons show significant physical and cognitive limitations with noticeable behavioral changes.
Here are the key factors that differentiate between being tipsy and drunk, along with their associated effects:
What Does It Feel Like to Be Drunk vs. Tipsy?
It feels like a mild, pleasant buzz when you are tipsy, and it feels like an overwhelming, disorienting state when you are drunk. When tipsy, you experience relaxed inhibitions, increased sociability, and a gentle euphoria while maintaining most motor functions and coherent thought. Conversations flow more easily, and you may feel more confident, though you might notice slight coordination changes and mild sensory dulling.
Being drunk feels substantially more intense than being tipsy. Drunk individuals experience pronounced physical symptoms, including significant dizziness, impaired balance, and compromised cognitive function. Speech becomes noticeably slurred, decision-making becomes poor, and walking becomes visibly unsteady. Physical discomfort often follows, including nausea, headaches, and general malaise. Emotionally, drunkenness can trigger mood swings ranging from excessive happiness to sadness or anger. The drunk state is typically remembered as physically uncomfortable and emotionally volatile compared to the more controlled tipsy experience.
What Are the Stages of Being Drunk?
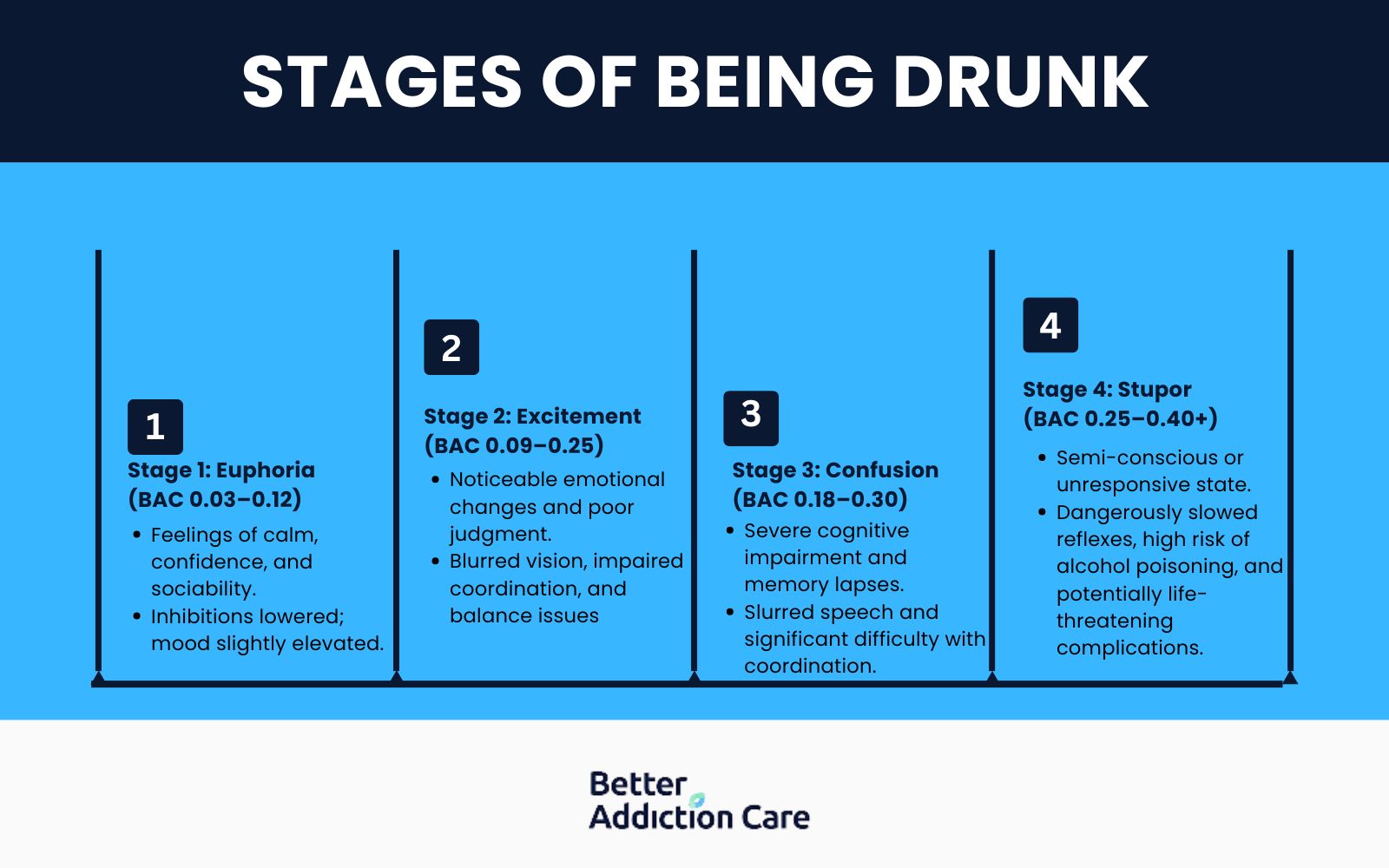
The stages of being drunk are euphoria, excitement, confusion, and stupor, influenced by several variables including body mass index (BMI), tolerance, metabolism, and individual differences. Blood alcohol content (BAC) provides a reliable way to classify these distinct phases of intoxication.
Here is how BAC levels provide information about the stages of being drunk:
-
Stage 1: Euphoria (BAC 0.03-0.12) - This initial stage is characterized by feelings of calm, friendliness, and mild mood enhancement. People experience decreased inhibitions, increased self-confidence, and more fluid social interactions.
-
Stage 2: Excitement (BAC 0.09-0.25) - During this stage, behavior becomes more pronounced. Note that 0.08 is the legal driving limit in most US states (0.05 in Utah). Symptoms include exaggerated emotions, blurred vision, balance difficulties, and impaired coordination and judgment, leading to poor decision-making and unpredictable social behavior.
-
Stage 3: Confusion (BAC 0.18-0.30) - At this stage, cognitive abilities are severely impaired. Individuals struggle to understand information, develop slurred speech, experience coordination problems, and suffer memory lapses. These impairments significantly increase risk factors.
-
Stage 4: Stupor (BAC 0.25-0.40+) - In this dangerous stage, people become semiconscious or completely unresponsive. Reflexes are severely weakened, creating serious risks of alcohol poisoning, respiratory depression, and choking on vomit—all potentially fatal outcomes.
These stages of drunkenness vary considerably between individuals. BAC measurements provide estimates, but many factors affect how alcohol impacts each person. Responsible drinking and knowing personal limits are essential for preventing harm to oneself and others.
Are There Legal Consequences for Being Drunk vs. Tipsy?
Yes, there are different legal consequences for being drunk versus being tipsy. The severity of these consequences depends on your level of intoxication, your behavior while under the influence, and the specific laws in your location.
When you're tipsy, you experience mild impairment of coordination and judgment. This level of intoxication rarely results in legal issues unless it leads to public intoxication, disorderly conduct, or impaired driving. However, if your impairment is noticeable and disturbs others or creates danger, you receive a citation.
Being drunk involves a more significant impairment of mental function. If you're visibly drunk and disruptive in public, you could face public intoxication charges. Behavior that disturbs the peace or violates others' rights while intoxicated results in disorderly conduct charges.
Driving while drunk or tipsy leads to DWI or DUI charges. Even being slightly above the legal blood alcohol content (BAC) limit results in severe penalties, including license suspension and possible jail time, depending on the jurisdiction.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), drunk driving caused 12,429 deaths in 2023. Alcohol-impaired crashes kill 34 people daily in the United States—one person every 42 minutes. Drunk drivers with a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of .08 g/dL or higher account for 30% of all U.S. traffic fatalities. Additionally, 2,117 people died in 2023 from crashes involving drivers with lower BAC levels (.01 to .07 g/dL). The ten-year data from 2014 to 2023 shows an average of 11,000 annual drunk-driving deaths. All these deaths were preventable.
Higher levels of intoxication increase aggression, potentially leading to assault charges or other violent crime allegations. Activities like drunk driving and public urination also result in public nuisance charges.
How Do Tipsy Drinkers Respond To Cage Guilt Questions?
Tipsy drinkers minimize guilt in CAGE questions despite experiencing remorse later. The CAGE Assessment reveals this contradiction through targeted questioning about emotional responses to drinking. Honest answers indicate awareness of problematic drinking patterns beneath casual dismissals.
Does Being Drunk Always Cause Alcohol Brain Fog?
Yes, being drunk always causes some level of Alcohol Brain Fog. When alcohol reaches your bloodstream, it immediately affects your brain function and creates brain fog that impairs cognitive abilities. The severity of this fog increases with higher blood alcohol concentration.
Even the morning after heavy drinking (when BAC is nearly zero), your brain's performance significantly declines. According to Gunn, C.’s 2018 study, ‘A systematic review of the next‐day effects of heavy alcohol consumption on cognitive performance, ’ In morning after a night of heavy drinking the short-term memory is 64% worse, long-term memory is 59% worse, sustained attention is 47% worse, and reaction speed is 66% slower than normal.
What Strategies Best Prevent Progression From Being Drunk To Alcohol Use Disorder?

Best strategies to prevent progression from being drunk to alcohol use disorder include setting clear drinking limits, practicing moderation, avoiding triggers that lead to excessive consumption, seeking professional guidance early, tracking alcohol intake patterns, and maintaining strong social support systems. These preventative measures significantly reduce the risk of developing Alcohol use disorder. Implementing these practices creates a protective barrier between occasional intoxication and the development of chronic alcohol use disorder.
How To Find Local Alcohol Rehab Facilities?
Finding local alcohol rehab facilities involves searching online directories, calling helplines, or using specialized treatment locators. Finding local alcohol rehab facilities involves searching online directories, calling helplines, or using specialized treatment locators. Numerous local alcohol rehab centers provide free assessments to help individuals struggling with alcohol use find the appropriate level of care. This includes options like in Florida, Texas, and New York. Additionally, community health departments and insurance providers offer updated lists of accredited treatment facilities available in your area.





