Phencyclidine Addiction: Definition, Causes, Signs, Effects, and Treatment Methods
Phencyclidine addiction is a state where people experience a dire need to use phencyclidine or PCP. PCP is a hallucination drug that leads to a false sense of reality.

Phencyclidine addiction is a state where people experience a dire need to use phencyclidine or PCP. PCP is a hallucination drug that leads to a false sense of reality.
The causes of Phencyclidine (PCP) addiction are genetics, trauma, environmental factors, peer pressure, lack of social support, poor coping skills, and mental health disorders.
The signs and symptoms of Phencyclidine (PCP) addiction are feelings of dependence, changes in physical appearance, lack of self-care, dilated pupils, flushed skin, excessive sweating, impaired fine motor skills, unusual behavior, isolated behavior, and relationship issues.
The side effects of Phencyclidine addiction are classified in two terms based on low to high-dosage use i.e. short-term effects and long-term effects.
The treatment methods for PCP addiction include detoxification, medication, cognitive behavioral therapy, inpatient and outpatient rehab, and support groups.
What is Phencyclidine Addiction?
Phencyclidine addiction is a condition when a person has a compulsive urge to take PCP. Phencyclidine or PCP was initially developed as an anesthetic drug in the 1960s but then discontinued due to its severe hallucinogenic effects. PCP creates mind-altering effects on intake including feelings of hallucinations and loss of control. The feeling of detachment from reality led PCP to be known as Angel Dust. PCP has some medicinal uses but a high risk for dependency and this is why it is regarded as a schedule II drug within the US, as per a document titled “PCP Fast Facts” by the National Drug Intelligence Center.
120,000 individuals aged 12 or older have used PCP in the year 2014. 2.4% of people in the US are addicted to PCP, as per a study titled “Facing Addiction in America: The Surgeon General's Report on Alcohol, Drugs, and Health.”
What is the other name of PCP?
The other names of PCP are angel dust, hog, boat, killer weed, peace pill, ozone, and wack. The names are often associated with the form and effect it creates. The names also reflect the ways it is consumed like smoked, injected, or snorted.
What does PCP look like?
PCP comes as a white crystalline powder and is found in the form of capsules, tablets, and liquids. PCP is often dyed to create varying colors. The powdered form is either fine or granular.
How is PCP used?
PCP is used by either smoking, injecting, or snorting. The liquid form of PCP is sprayed onto cigarettes for smoking purposes and the powdered form is snorted through the nose. PCP is injected into the bloodstream in liquid form as well.
How quickly does PCP kick in?
PCP kicks in within 15 to 30 minutes when smoked or injected while it takes 5 to 10 minutes to kick in when snorted. The fastest kick-in happens with the snorted method as it has a direct way of absorption through the nasal way.
What are the causes of Phencyclidine Addiction?
The causes of Phencyclidine (PCP) addiction are genetics, trauma, environmental factors, peer pressure, lack of social support, poor coping skills, and mental health disorders.

The causes of PCP addiction are listed below:
-
Genetics: Genetics determine a person’s PCP tolerance and risk of dependence levels. A person with a family history of substance abuse is more likely to be addicted to PCP upon usage.
-
Trauma: Trauma leads to ongoing emotional pain that results in using PCP as a source of relief. People who have suffered some form of trauma like neglect, abuse, or the death of a loved one are likely to get addicted to PCP.
-
Environmental factors: Environmental factors like societal behaviors and ease of access increase the chance of PCP addiction. People who have PCP readily available are known to be dependent on its usage, as per a study titled “Facing Addiction in America: The Surgeon General's Report on Alcohol, Drugs, and Health.”
-
Peer pressure: Peer pressure leads people to try PCP to fit in or get accepted in a certain social group. The initial testing results in long-term effects and PCP addiction.
-
Lack of social support: People having less social support tend to be isolated and use PCP to diminish emotional distress. The constant usage becomes a cause for PCP addiction.
-
Poor coping skills: People coping with stress and trauma poorly are likely to rely on PCP as a source of ease. The poor way of coping leads to continuous reliance on it, resulting in PCP addiction.
-
Mental health disorder: PCP is used as a self-medication to find relief from the symptoms of mental health disorders like anxiety and depression. The irregular doses result in PCP addiction.
What are the Signs of Phencyclidine Addiction?
The signs and symptoms of Phencyclidine (PCP) addiction are feelings of dependence, changes in physical appearance, lack of self-care, dilated pupils, flushed skin, excessive sweating, impaired fine motor skills, unusual behavior, isolated behavior, and relationship issues.

The signs of PCP addiction are listed below:
-
Feeling of dependence: People with PCP addiction find themselves physically and psychologically dependent on it. The unavailability of dosage creates an unsettling feeling.
-
Changes in physical appearance: People with PCP addiction tend to show their habits in appearance through weight loss and pale skin.
-
Lack of self-care: Individuals with PCP addiction lose the sense of self-care especially when it comes to personal hygiene. Poor hygiene habits like not taking a shower, wearing the same clothes for days, or not brushing hair are indicators of PCP addiction.
-
Dilated pupils: PCP addiction leads to dilated pupils as they become less constricted in response to usage.
-
Flushed skin: Poor hygiene habits due to PCP addiction result in dirt accumulation in the skin. Flushed and pale skin are common indicators of PCP addiction.
-
Excessive sweating: People with PCP addiction suffer from shaky hands and excessive sweating due to loss of muscle control after usage.
-
Impaired fine motor skills: PCP creates hallucinogenic effects that result in impaired motor skills. People have difficulty finding balance and appear clumsy.
-
Unusual behavior: People with PCP addiction often exhibit unusual and secretive behavior to gain excess to the drug or use it.
-
Isolated behavior: PCP addiction makes people isolated and neglect their relationships. Individuals losing interest in activities and relationships are likely to be PCP addicts.
-
Relationship issues: The isolation and neglect after PCP usage results in broken relationships. People with PCP addiction tend to separate themselves from social gatherings.
What are the side effects of Phencyclidine Addiction?
The side effects of Phencyclidine addiction are classified in two terms based on low to high dosage use i.e. short-term effects and long-term effects.
The side effects of PCP addiction are listed below:
Short-term effects of use:
The short-term effects of phencyclidine are subdivided into low to moderate doses and high doses based on the dosage of the substance.
Low to moderate doses:
Low to moderate doses of PCP addiction are listed below:
-
Numbness: A low dose of PCP causes a loss of senses and a brief feeling of numbness in the limbs. The feeling is similar to floating and body detachment.
-
Slurred speech: The disturbed motor control after PCP usage results in impaired and slurred form speech.
-
Lack of muscle coordination and balance: PCP causes motor skills impairment that results in poor muscle coordination. The cognitive and muscle imbalance makes the person addicted to PCP appear clumsy.
-
Impaired concentration or speech: The hallucinogenic effects of low doses of PCP lead to a lack of focus. People become unable to keep their concentration straight.
-
Racing heartbeat: PCP is known to stimulate the heart. The moderate dosage results in a fast heartbeat rate.
-
Excessive sweating: Low doses of PCP increase the body temperature enough to cause excessive sweating.
-
Rapid, involuntary eye movements: PCP intake makes people create an alert state of consciousness leading to rapid eye movements.
-
Blank stares: PCP usage leads to a lack of focus and impaired cognitive skills that result in people staring into the abyss.
High dose effects:
High dose effects of PCP addiction are listed below:
-
Hallucinations: Higher doses of PCP are known to cause hallucinations that are terrifying. People tend to become paranoid and aggressive as a result, as per a study titled “PCP and Hallucinogens” by Marilyn E. Carroll PhD.
-
Flashbacks: People with PCP addiction suffer from flashbacks with disturbing visuals or altered perceptions. The flashbacks often come after 3 to 4 days of PCP intake.
-
Shallow breathing: High doses of PCP cause respiratory distress that results in rapid or shallow breathing patterns.
-
High temperature: People taking PCP in high doses often experience a temperature rise that results in excessive sweating.
-
High blood pressure: PCP in higher doses leads to cardiac distress that results in high blood pressure and rapid heartbeat.
-
Nausea and vomiting: Higher doses of PCP often cause a disturbed gastrointestinal state that results in the feeling of nausea and vomiting.
-
Dizziness The impaired motor coordination after using higher doses of PCP results in a feeling of dizziness and fainting.
Long-term effects of use
The long-term effects of phencyclidine are memory loss, synesthesia, paranoia, delusional thoughts, weight loss, and self-injury.
-
Memory loss: The long-term usage of PCP leads to cognitive impairment that results in memory loss and trouble making decisions. The cognitive impairment disrupts daily life functioning.
-
Synesthesia: The consistent usage causes complications in perceptions of reality resulting in synesthesia. People tend to mix two sensations as they start to see sounds and taste colors.
-
Paranoia: Long-term use of PCP causes psychological problems like anxiety, distress, and depression that results in paranoia and hallucinations.
-
Delusional thoughts: The constant hallucinations after PCP usage results in a delusional state of mind. The delusions detach the person from thoughts of reality.
-
Weight loss: Long-term usage of PCP leads to appetite suppression and poor hygiene practices resulting in major weight loss.
-
Causes self-injury: Long-term PCP usage makes people have poor cognitive judgment leading to risks of self-injury.
What are the Risk Factors for Overdose of Phencyclidine Addiction?
The risk factors for overdose of Phencyclidine addiction are often psychological, environmental, physical, and emotional. People taking higher doses of PCP or mixing it with other substances to intensify effects are likely to experience overdose. History of substance abuse and underlying mental health disorders like anxiety and depression are common overdose risk factors for PCP addiction.
What are the withdrawal symptoms of Phencyclidine Addiction?
The withdrawal symptoms of PCP are cravings for PCP, headaches, sweating, increased appetite, and depression. Phencyclidine withdrawal is a state of physical and psychological reactions a person experiences after reducing or diminishing the usage of phencyclidine.
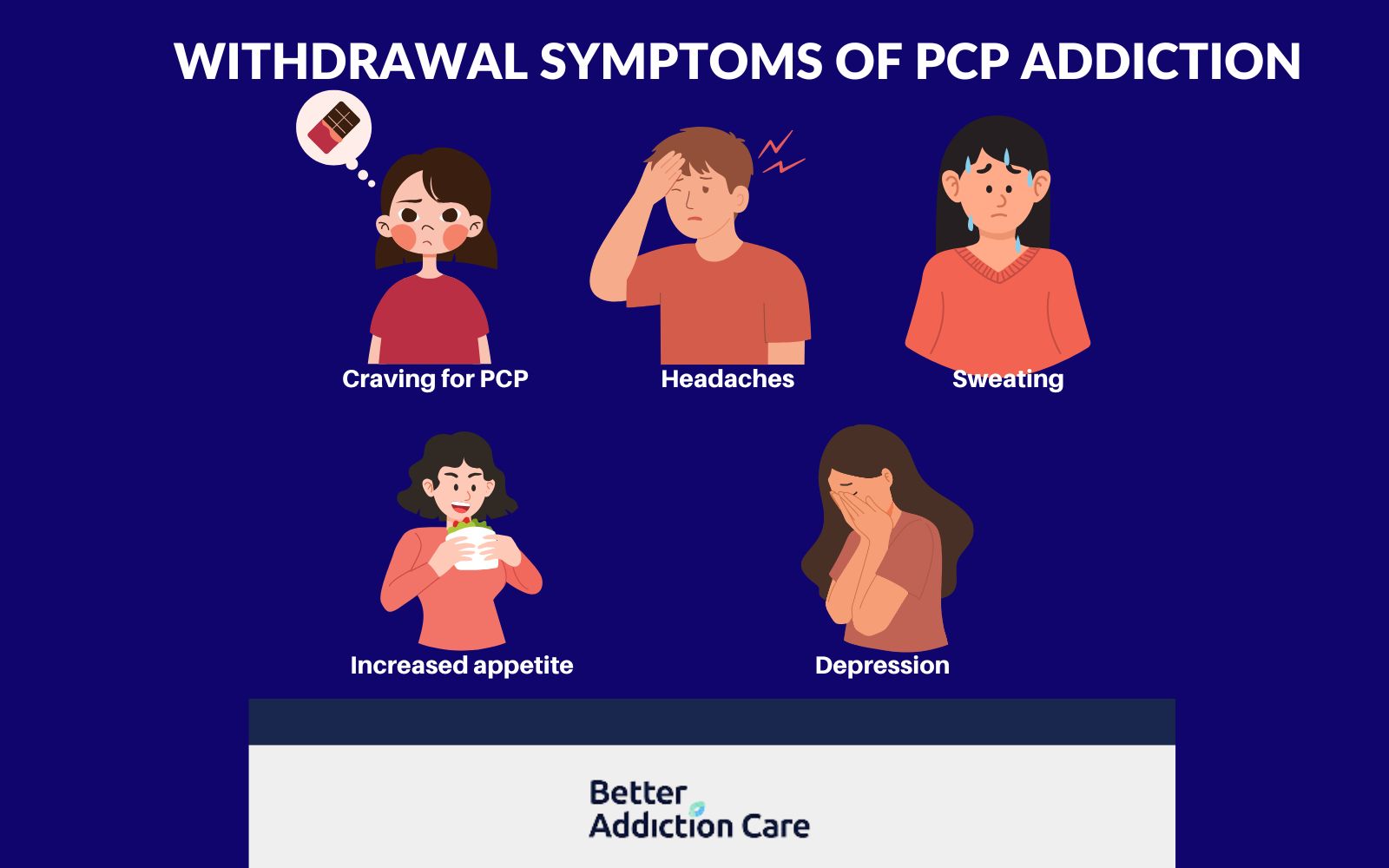
The withdrawal symptoms of PCP addiction are listed below:
-
Craving for PCP: The sudden dosage reduction of PCP makes people crave for PCP. The craving is often strong and persistent which makes it difficult for people to stop PCP usage.
-
Headaches: PCP withdrawal often leads to disturbed brain chemistry and overall distress that results in constant headaches.
-
Sweating: After the absence of PCP, the body tries to regulate temperature back to normal which results in excessive sweating and shaky hands.
-
Increased appetite: People neglecting their health during drug usage often experience increased appetite after withdrawal to compensate for nutritional needs.
-
Depression: After withdrawal, people often experience mental distress that leads to several disorders like anxiety and depression.
What are the treatment methods for PCP addiction?
The treatment methods for PCP addiction include detoxification, medication, cognitive behavioral therapy, inpatient and outpatient rehab, and support groups.

The treatment options for PCP addiction are listed below:
-
Detoxification: Detoxification is a medically assisted treatment that helps to get rid of PCP toxins from the body. The detoxification process takes up to 2 to 4 weeks.
-
Medication: There is no specific medication directed for PCP addiction but the root causes like mental health disorders are addressed with it. Medicines like antidepressants are advised by a medical expert to reduce the risk factors of PCP addiction.
-
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: CBT helps to address the root causes of PCP intake. Counselors attempt to alter the thought processes and behaviors leading to drug usage. The sessions last up to 3 to 6 months, as per a study titled “Phencyclidine Toxicity” by Jonathan D. Journey.
-
Inpatient and outpatient rehab: Rehab programs offer monitored care to people addicted to PCP in a controlled environment. Rehab is done either at home with a personalized approach or at a specialized rehab center. Rehab takes almost 3 to 4 months as per the condition of the person, as per a study titled “Outpatient treatment of PCP abusers” by D A Gorelick.
-
Support groups: Support groups offer people a gathering of shared experiences that make recovery and finding help easier. The recovery with support groups takes several months to a year.
How Does Phencyclidine Addiction Relate to Other Substance Addictions?
Phencyclidine addiction relates to other substance addictions in ways like risk factors, psychological experiences, dependence, and co-occurring mental health conditions. PCP addiction has similarities with the addiction of other substances including alcohol, stimulants, opioids, and hallucinogens.
Does phencyclidine addiction differ from opioid addiction in effects and risks?
Yes, phencyclidine addiction differs from opioid addiction in effects and risks. PCP is known to block brain receptors while opioids bind to brain receptors. PCP addiction causes hallucinations and opioid addiction effects include pain relief and euphoria.
Do phencyclidine addiction and Xanax addiction have the same effects?
No, phencyclidine addiction and Xanax addiction don’t have the same effects because phencyclidine addiction creates an effect of hallucinations and detachment from reality. Xanax addiction leads to a calming and sedating effect on the brain.







