Pregabalin Addiction: Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Effects, and Treatment Options
Pregabalin addiction is a state of an uncontrollable urge to use pregabalin for relief or recreational purposes. Pregabalin is a medicinal drug prescribed for the treatment of epilepsy and anxiety disorders.

Pregabalin addiction is a state of an uncontrollable urge to use pregabalin for relief or recreational purposes. Pregabalin is a medicinal drug prescribed for the treatment of epilepsy and anxiety disorders.
The causes of pregabalin addiction are co-occurring substance abuse, co-occurring mental conditions, pregabalin tolerance, self-medication, accessibility, and environmental influences.
The symptoms of pregabalin addiction are surpassing the recommended doses, increased tolerance, non-medical pregabalin use, mixing with other drugs, intense cravings, loss of control, and secretive behavior.
The side effects of pregabalin addiction are dizziness, fatigue, impaired balance, blurred vision, tremor, lethargy, weight gain, memory problems, and euphoria.
The available treatment options for pregabalin addiction are detoxification via medicines, inpatient or outpatient rehab, counseling, therapy, support groups, dual diagnosis treatment, and aftercare.
What is Pregabalin Addiction?
Pregabalin addiction is a state where people have the urge to take pregabalin uncontrollably with or without a prescription. Pregabalin is an anticonvulsant medicine used to treat epilepsy & anxiety disorders. Pregabalin is prescribed in a controlled amount and intake beyond the prescribed amount leads to addiction. Pregabalin comes under the medical names Lyrica and Lyrica CR, as per a study titled “A case of pregabalin addiction” by Samiksha Sahu.
How Common is Pregabalin Addiction?
Pregabalin addiction is very common because approximately 0.1% of the population in the US was found to have pregabalin addiction in the year 2021, as per the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). Pregabalin addiction rates are lower in contrast to other substance addictions leading to less available stats.
What is the difference between Pregabalin and Gabapentin Addiction?
The difference between pregabalin and gabapentin lies in their chemical structure, working, dosage, approved usage, and side effects. Pregabalin and gabapentin are both FDA-approved medicines prescribed to treat nerve pain. The medicines are similar yet there are differences. Pregabalin has higher potency than gabapentin which makes it work faster at low dosages. Gabapentin absorbs at a slower rate than pregabalin. Pregabalin potentially leads to peripheral edema while gabapentin misuse leads to gastrointestinal issues, as per a study titled “How addictive are gabapentin and pregabalin? A systematic review” by U Bonnet.
What are the causes of Pregabalin Addiction?

The causes of pregabalin addiction are co-occurring substance abuse, co-occurring mental conditions, pregabalin tolerance, self-medication, accessibility, and environmental influences.
The causes of pregabalin addiction are listed below:
-
Co-occurring substance abuse: Individuals who are already misusing other addictive substances are more prone to be pregabalin addicts. The brain is dependent on substances and requires variables and high doses. The usage of pregabalin in this situation leads to addiction.
-
Co-occurring mental conditions: Pregabalin has a calming and mood-stabilizing effect on the brain. People suffering from mental health conditions like anxiety and depression find relief by using Pregabalin. The continuous urge for this relief leads to pregabalin addiction.
-
Pregabalin tolerance: The continuous usage of pregabalin increases its tolerance in the body. The increased tolerance requires higher doses for the same effect as earlier. The higher doses of pregabalin result in pregabalin addiction, as per a study titled “Pregabalin: its efficacy, safety, and tolerability profile in generalized anxiety” by Richard T Owen.
-
Self-medication: People often use pregabalin to treat depression or anxiety-related disorders on their own. The unsupervised usage of pregabalin with varying doses poses a higher risk of getting addicted to it.
-
Accessibility: The constant availability, easy access, and intake of pregabalin make the brain dependent on pregabalin. The dependent state makes people addicted to it. The dependence does not reduce until the access is stopped.
-
Environmental influences: Environmental factors like peer pressure, family dynamics, and stress are common causes of pregabalin addiction. A person facing issues in life or surrounded by people addicted to pregabalin is more likely to develop its addiction themselves, as per a study titled “Pregabalin Addiction: A Bibliometric Analysis” by Fatma Gül Sak.
What are the symptoms of Pregabalin Addiction?

The symptoms of pregabalin addiction are surpassing the recommended doses, increased tolerance, non-medical pregabalin use, mixing with other drugs, intense cravings, loss of control, and secretive behavior.
The symptoms of pregabalin addiction are listed below:
-
Surpassing the recommended doses: Intaking more than prescribed doses of pregabalin is a sign that the person is addicted to it. This urge to increase the effect of pregabalin on the brain makes a person take more than the required doses, leading to addiction.
-
Increase tolerance: The continuous use of pregabalin increases its tolerance in the body. The lesser effect of the current dosage means the tolerance has increased which is a common sign of getting addicted to pregabalin.
-
Non-medical pregabalin use: Pregabalin is only used under prescription for monitored use as it has the potential for addiction. Using pregabalin without prescription and for recreational purposes is a sign of pregabalin addiction, as per a study titled “Non-medical Use of Prescription Gabapentinoids (Gabapentin and Pregabalin) in Five European Countries” by Francina Fonseca.
-
Mixing with other drugs: People tend to mix various drugs for an increased or intense effect on the brain. A person mixing pregabalin with other drugs means he is addicted to pregabalin.
-
Intense cravings: Individuals getting intense cravings for using pregabalin for relief are usually addicted to it. Pregabalin addiction leaves a person with a constant urge for more intake.
-
Loss of control: Individuals with pregabalin addiction are not completely in control of their drug usage. The cravings and intake simultaneously increase. Pregabalin addiction leads to health issues but people addicted to it are not able to stop the usage.
-
Secretive behavior: Individuals addicted to pregabalin tend to keep their intake and usage secret. They try to steal money or lie for prescriptions to get more doses of pregabalin.
What are the side effects of Pregabalin Addiction?

The side effects of pregabalin addiction are dizziness, fatigue, impaired balance, blurred vision, tremor, lethargy, weight gain, memory problems, and euphoria.
-
Dizziness: Pregabalin affects the central nervous system (CSN), leading to a dizzy state of mind. Increased doses due to pregabalin addiction result in excessive dizziness.
-
Fatigue: Pregabalin addiction leads to a sedative state that weakens the muscles. The constant usage leaves the body in pain and fatigue.
-
Impaired balance: Pregabalin addiction affects the overall senses and leads to delayed reactions and poor muscle control. The condition leads to impaired muscle control.
-
Blurred vision: Pregabalin affects neurotransmitters in the brain that make it difficult to keep the vision stable. Pregabalin addiction leads to a blurry state of vision.
-
Tremor: The use of pregabalin leads to uncontrolled muscle control that results in shaky movements especially related to the limbs.
-
Lethargy: Pregabalin addiction acts as a sedative on the brain that makes the body feel sluggish and drowsy. The constant feeling of sluggishness results in tiredness and lethargy.
-
Weight gain: Pregabalin addiction increases appetite, leading to excessive calorie intake. Over time, this excess calorie intake results in weight gain, which is more likely to be visible in the limbs, as per an article on Pregabalin by the NHS.
-
Memory problems: Pregabalin use affects the brain and disturbs the neurochemicals that impact memory.
-
Euphoria: Pregabalin creates a sedative effect on the brain leading to a state of euphoria. Higher doses of pregabalin cause a greater sense of pleasure and euphoria.
What are the withdrawal symptoms of Pregabalin Addiction?
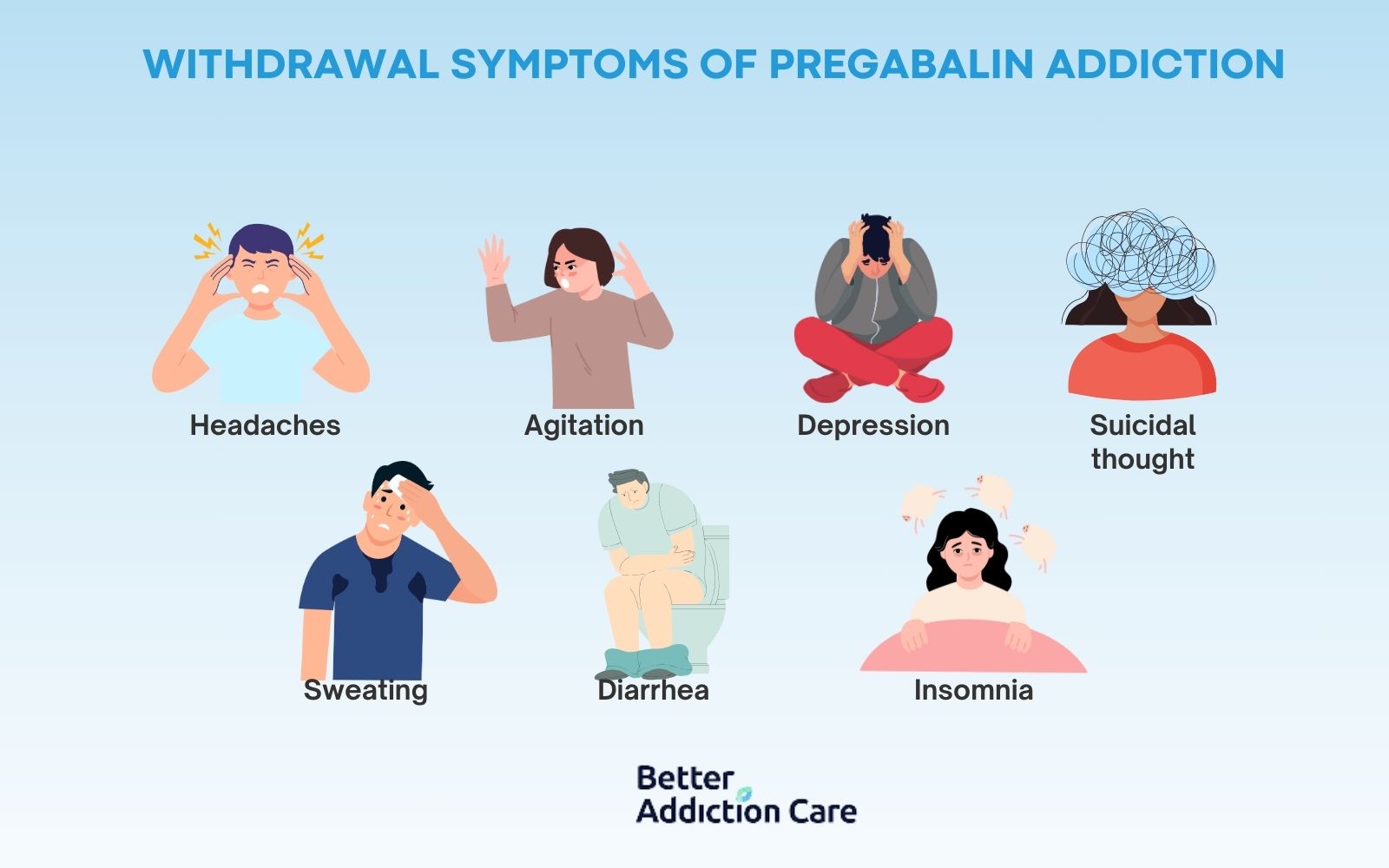
The withdrawal symptoms of pregabalin addiction include headaches, mood changes, agitation, depression, suicidal thoughts, sweating, diarrhea, and insomnia. Pregabalin withdrawal is a state of psychological and physical reactions of the body when a person suddenly stops or reduces the intake of pregabalin.
The withdrawal symptoms of Pregabalin addiction are listed below.
-
Headaches: When a person stops taking pregabalin, it triggers a constant throbbing in the head leading to headaches. Pregabalin acts on the neurotransmitters in the brain. When the dose reduces there’s a neurotransmitter imbalance that leads to headache.
-
Agitation: The sudden reduction of pregabalin causes mood instability including a feeling of irritation or agitation. The brain and body become dependent on pregabalin. The disturbance in this pattern causes agitation.
-
Depression: The pregabalin withdrawal affects the neurotransmitter's activity. The imbalance leads to mental health disorders like anxiety and depression, as per a study titled “Pregabalin withdrawal in patients without psychiatric disorders taking a regular dose of pregabalin: A case series and literature review” by Hayahito Ishikawa.
-
Suicidal thought: The constant depressive episodes due to withdrawal result in extreme thoughts like suicide. Treatment is essential to reduce the frequency of these thoughts.
-
Sweating: When the pregabalin dose is suddenly reduced or restricted the body stabilizes the neurotransmitters resulting in symptoms like sweating and shaky hands.
-
Diarrhea: Pregabalin withdrawal leads to gastrointestinal issues, such as diarrhea and constipation. It takes time before a person’s eating patterns come back to normal after withdrawal disturbances.
-
Insomnia: The disturbed state of mind after pregabalin withdrawal makes people unable to sleep properly, leading to unhealthy sleep patterns and insomnia.
What are the Treatment Options for Pregabalin Addiction?
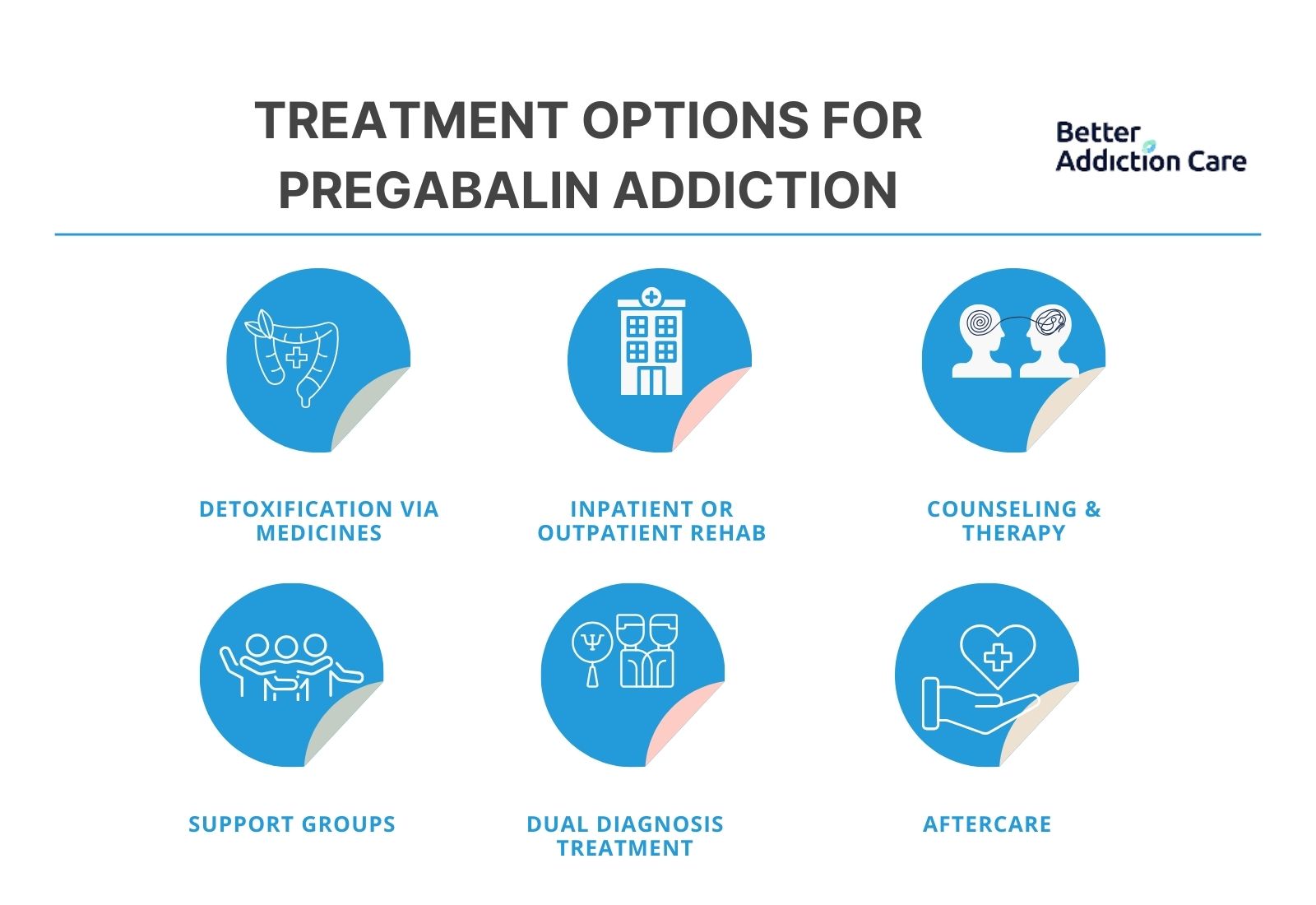
The treatment options for pregabalin addiction are detoxification via medicines, inpatient or outpatient rehab, counseling, therapy, support groups, dual diagnosis treatment, and aftercare.
-
Detoxification via medicines: Detoxification through medicines helps the body get rid of pregabalin toxins. Detoxification like this supports gradual treatment that allows the body to slowly adjust to pregabalin withdrawal. Detoxification takes up to 2 to 3 months for recovery.
-
Inpatient or outpatient rehab: Inpatient or outpatient rehab programs help in recovery through a monitored and clinically proven approach. Rehab programs are available within a rehab center or at home as preferred. The duration ranges from a few weeks to months depending on the choice of program.
-
Counseling & therapy: Therapy sessions with a medical expert help to treat the root cause of pregabalin addiction. A counselor or therapist holds regular sessions and finds the best treatment based on the medical history, substance abuse, and current symptoms, as per a study titled “A case of pregabalin addiction” by Samiksha Sahu.
-
Support groups: Support groups help to recover from pregabalin addiction by providing a platform for shared experiences. People talk about their struggles and journey under an expert’s supervision which leads to gradual healing with medications. The treatment duration with support groups ranges from 3 to 4 months.
-
Dual diagnosis treatment: Dual diagnosis treatment is for people suffering from Pregabalin addiction and mental health disorders simultaneously, such as anxiety and depression. Dual diagnosis treatment involves a combination of medications and counseling sessions and takes up to 1 to 3 months depending on the condition.
-
Aftercare: Aftercare is the most essential part of treatment due to the fear of relapse. Aftercare helps to stop people from going back to pregabalin addiction.
What are the complications of Pregabalin Addiction?
The complications of Pregabalin addiction are usually physical, psychological, and social. Physical complications include health problems, drowsiness, shaky hands, and fatigue. Psychological complications include the onset or progression of mental health disorders like depression and anxiety. Social complications include isolation, neglect of responsibilities, financial strain, and disturbed relationships.
How Does Pregabalin Addiction Relate to Other Substance Addictions?
Pregabalin addiction relates to other substance addictions in terms of effects, usage, and mechanisms of dependence. Pregabalin acts on the CNS (Central Nervous System) and creates relaxing and euphoric effects similar to opioids and stimulants.
Do pregabalin and crystal meth have the potential for misuse?
Yes, Pregabalin and crystal meth have the potential for misuse. Pregabalin is a medicine used to treat epilepsy and anxiety. Crystal meth is a central nervous system stimulant that increases dopamine release. Pregabalin is often misused for a calming effect, while crystal meth addiction is related to euphoric effects.
Can users of pregabalin and benzodiazepines experience feelings of euphoria or relaxation?
Yes, users of pregabalin and benzodiazepines can experience feelings of euphoria or relaxation. Benzodiazepines are central nervous system depressants that increase the binding of neurotransmitters GABA. Benzodiazepine addiction causes a feeling of enduring euphoria. Pregabalin also impacts the GABA levels and leads to a sensation of euphoria and relaxation.
Can pregabalin and marijuana lead to physical dependence?
Yes, Pregabalin and marijuana can lead to physical dependence. Marijuana is a mind-altering drug that creates a calming and relaxing feeling in the brain. Marijuana leads to physical dependence but frequency is lower. Pregabalin is used to treat anxiety and epilepsy. Pregabalin addiction is more common than marijuana addiction, especially at higher doses.
Related Articles
Treatment Centers in Colorado










