Alcohol Cravings: Definition, causes, Management and Rehab Centers
Alcohol cravings are intense urges to drink, common in those with alcohol dependence. According to a report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) titled "Data on Excessive Alcohol Use published in 2024", 17% of U.S. adults binge drink and 6% drink heavily, with nearly all heavy drinkers also engaging in binge drinking. The same report notes that over 90% of adults who drink excessively report binge drinking, highlighting its prevalence. In another CDC publication titled "Alcohol Use and Your Health released" in 2025, it is explained that binge drinking episodes can be triggered by internal emotions and external alcohol-related cues, and may cause physical symptoms such as restlessness and sweating, and psychological symptoms like intense emotions. These episodes typically last 15–20 minutes and are more frequent during early recovery

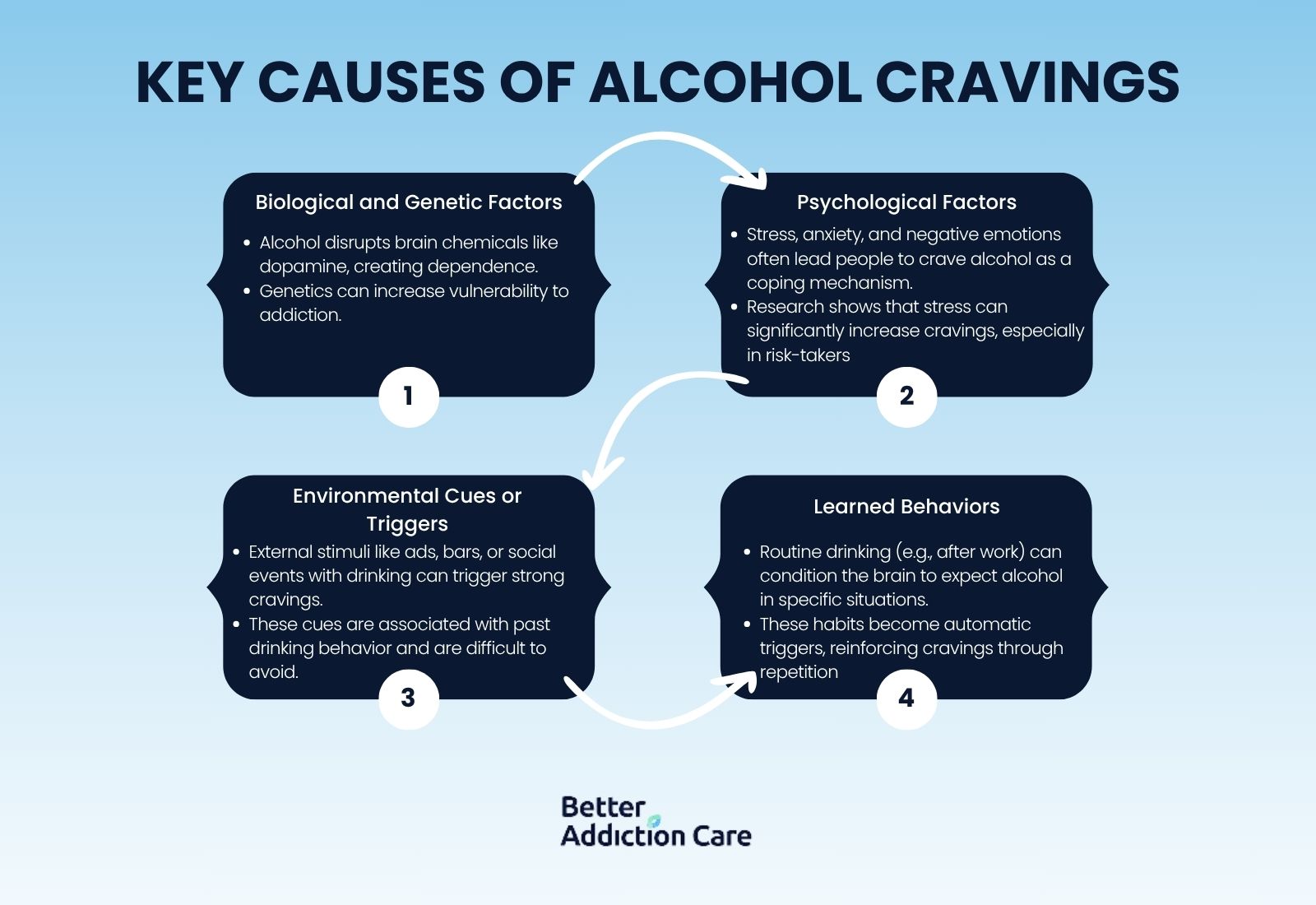
Alcohol cravings are caused by disruptions in brain chemistry, particularly dopamine levels, along with genetic factors, stress, emotional triggers, and environmental cues. These elements create a dependence on alcohol by linking its consumption with pleasure and reinforcing learned behaviors.
To manage cravings, identify triggers, and develop avoidance strategies. Utilize immediate coping techniques to distract yourself during cravings and adopt sustainable lifestyle changes, such as mindfulness and exercise, to reduce their frequency. Consider seeking professional support, including therapy and medication-assisted treatment.
What Are Alcohol Cravings?
Alcohol cravings are powerful and sometimes uncontrollable urges to drink alcohol. They are frequently observed among people who have developed alcohol dependence or are long-time users.
Physically, alcohol cravings are likely to present symptoms such as restlessness, sweating, shaking, increased heartbeat, and a general feeling of uneasiness or discomfort. Psychologically, cravings provoke strong emotions and intrusive thoughts, making it harder to focus on something else.
These cravings are usually time-limited, lasting 15-20 minutes on average, and are more frequent in the early stages of recovery.
Cravings occur spontaneously or are triggered by internal or external stimuli, known as cues. Internal cues include emotional states, like anxiety or symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal. External cues include exposure to alcohol-related environments or objects, like bottles of alcoholic beverages or advertisements.
What Causes Alcohol Cravings?
Causes of alcohol cravings include brain chemistry disruptions affecting dopamine levels, genetic predisposition to addiction, stress and emotional triggers, environmental cues like social settings, and established drinking routines. These factors work together to create powerful urges that are difficult to resist without proper understanding and intervention.
Listed below are 4 main causes of alcohol cravings.
- Biological and Genetic Factors
- Psychological Factors
- Environmental Cues and Triggers
- Learned Behavior
1. Biological and Genetic Factors
Biologically, the brain chemistry is the most significant factor in causing alcohol cravings. Drinking alcohol interferes with levels of neurotransmitters, particularly dopamine, which is associated with pleasure and reward. The brain’s reward system is affected, leading to a pleasurable sensation every time alcohol is consumed, creating alcohol dependence to release dopamine, which results in cravings when alcohol is unavailable.
This creates a loop where the brain connects alcohol to pleasure and restlessly anticipates it.
Apart from affecting the levels of dopamine, alcohol intake also alters the levels of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and GABA, which regulate emotions. This disruption contributes to symptoms like brain fog, with consequences, such as making it harder for individuals to think clearly and manage their cravings effectively.
Another factor is genetics. Certain individuals are genetically predisposed to easily develop alcohol cravings. For instance, a person with a family history of alcoholism or a gene that increases the risk of addiction is more likely to experience these cravings.
2. Psychological Factors
Psychological factors like stress and emotional triggers cause alcohol cravings. Many individuals rely on alcohol for relief from stress, anxiety, and negative feelings. This reliance creates alcohol dependence to manage these emotions, leading to increased cravings in similar situations.
According to Clay, J. M.’s 2018 study, ‘Psychosocial stress increases craving for alcohol in social drinkers: Effects of risk-taking’, exposure to stress significantly increased alcohol cravings (with a confidence interval of 1.2-17.2 points), with researchers finding that those who take more risks showed greater increases in craving after stressful situations.
3. Environmental Cues or Triggers
Environmental cues like seeing alcohol advertisements, walking past bars, or being around friends, family, or acquaintances who are drinking sparks strong cravings to drink alcohol. Social settings where alcohol is present frequently serve as powerful reminders of past habits, reinforcing the urge to participate. These external triggers for alcohol include specific places, people, and situations linked to previous drinking behavior, making them critical to identify and manage in recovery.
4. Learned Behaviors
Learned behavior increase the craving for alcohol, for example if a person has established a routine of having a drink after work every evening, the end of the workday might spark the urge for an alcoholic drink. Such habituated reactions are potent and hard to overcome.
What are ways to stop Alcohol Cravings And Withdrawals?
You can stop alcohol cravings and withdrawals effectively by focusing on recognizing personal triggers, implementing avoidance strategies, utilizing immediate coping techniques, making sustainable lifestyle modifications, and accessing professional support when necessary.
Listed below are 5 ways of managing alcohol cravings and withdrawals.
- Identify your triggers
- Develop a trigger avoidance plan
- Use immediate coping strategies during cravings
- Adopt log term life style changes
- Seek Professional help when needed.
1. Identify Your Triggers
Cravings are triggered by internal or external cues. These include:
-
Emotional states like stress, anxiety, or loneliness
-
Environmental factors such as seeing alcohol, being in bars, or attending social events where drinking is common
-
Learned behaviors, like having a drink after work
Recognizing your triggers is the first step to managing them. Reflect on situations that lead to strong urges to drink and use this awareness to guide your next steps.
2. Develop a Trigger Avoidance Plan
Once you’ve identified your triggers, create a plan to avoid or minimize exposure to them. For example:
-
Attend fewer social gatherings where alcohol is present
-
Distance yourself from people or environments that encourage drinking
-
Keep alcohol out of your home
-
Choose alcohol-free venues when socializing
Creating a supportive environment significantly reduces the likelihood of cravings.
3. Use Immediate Coping Strategies During Cravings
Alcohol cravings are usually short-lived, typically lasting 10–20 minutes. Use these techniques to manage them:
-
Acknowledge the craving without judgment and remind yourself it will pass.
-
Redirect your attention with distraction techniques:
-
Go for a walk or engage in light exercise
-
Call a friend or family member
-
Listen to music or a podcast
-
Read, take a bath, or watch a movie
-
Prepare a snack or tea
These simple actions help shift focus away from the urge to drink.
4. Adopt Long-Term Lifestyle Changes
Adopt a long-term lifestyle change to reduce the frequency and intensity of cravings over time by:
- Practice mindfulness techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to observe cravings without acting on them
-
Engage in daily physical activity — regular exercise boosts mood and reduces stress
-
Explore hobbies or creative outlets such as gardening, cooking, journaling, or music therapy
-
Practice mindful eating to enhance emotional regulation and satisfaction
-
Join a support group like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or SMART Recovery for peer encouragement and accountability
5. Seek Professional Help When Needed
If cravings or withdrawal side effects and symptoms feel overwhelming, professional treatment provides essential support by giving you medication assisted treatment or therapy.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) Alcohol Rehab
Certain medications help reduce cravings and ease withdrawal such as the list below.
-
Naltrexone blocks opioid receptors to reduce the rewarding effects of alcohol
-
Acamprosate stabilizes brain chemistry and eases withdrawal discomfort
-
Disulfiram causes unpleasant reactions if alcohol is consumed, discouraging use
-
Topiramate helps regulate brain function and reduce cravings
For individuals struggling with severe alcohol dependency, medically assisted alcohol rehab provides the comprehensive medical supervision and pharmaceutical support necessary for safe and effective recovery.
Therapy and Counseling
Behavioral therapies equip individuals with tools to manage cravings and prevent relapse such as the list below.
-
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps identify and change harmful thought patterns
-
Motivational Enhancement Therapy (MET) strengthens motivation for change
-
Contingency Management (CM) reinforces positive behavior through incentives
-
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) improves emotional regulation
-
12-Step Facilitation encourages participation in recovery groups
-
Family Therapy supports healing within relationships
Working with a licensed therapist or addiction specialist ensures personalized care and long-term success.

How To Find A Local Alcohol Rehab Facility Near Me?
To find a local alcohol rehab facility near you, start by asking your primary care physician, therapist, or mental health professional for referrals to reputable treatment centers in your area. Contact your insurance provider to obtain a list of covered facilities, reach out to local hospitals and community health centers for recommendations, and connect with support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous for peer guidance.
Additionally, utilize online treatment locators and directories that allow you to filter results by location, treatment type, and insurance acceptance. Research each facility's credentials, treatment approaches, and patient reviews, then call directly to discuss their programs, availability, and admission requirements.
Conclusion
Whether you’re exploring options near home or in a new environment, our listings include rehab facilities in California, Texas, Georgia, Massachusetts and any more. For personalized assistance, call our helpline at (888) 766-0149 and take advantage of our free insurance verification service to better understand your coverage before starting treatment.
At Better Addiction Care, we understand the importance of connecting individuals with the right treatment resources. Our comprehensive database helps you locate alcohol rehab facilities across the country that align with your specific needs, insurance coverage, and location preferences. You’ll find detailed information about each center’s treatment methods, amenities, and areas of specialization, empowering you to make an informed choice.
Related Articles
Treatment Centers in Pennsylvania










