How to Get Sober after years of Alcohol Abuse: Stages, Relapse and After Care
Getting sober after years of alcohol abuse is a transformative path where individuals must face chronic physiological damage, emotional instability, and social disconnection, and apply structured treatment, commitment, and resilience to rebuild their lives. With 61.4 million Americans binge drinking monthly, recovery begins by admitting unmanageability and seeking professional guidance, leading to medically supervised detox and individualized care plans.

Getting sober after years of alcohol abuse is a transformative path where individuals must face chronic physiological damage, emotional instability, and social disconnection, and apply structured treatment, commitment, and resilience to rebuild their lives. With 61.4 million Americans binge drinking monthly, recovery begins by admitting unmanageability and seeking professional guidance, leading to medically supervised detox and individualized care plans.
The process moves through 7 stages of pre-contemplation, acknowledgment, preparation, action, and maintenance, each reflecting varying levels of dependence, motivation, and support needs. Relapse often signals unresolved triggers and calls for strengthening coping strategies. At Better Addiction Care, aftercare includes personalized therapy, peer support, and relapse prevention, ensuring sustained sobriety through routine reinforcement, risk awareness, and connection to community.
How to Get Sober?
Getting sober begins when the individual acknowledges the impact of alcohol misuse and commits to professional intervention and structured recovery. The journey starts with recognizing unmanageability and undergoing a medical evaluation to assess physical and psychological risks. This leads to a personalized detox plan that ensures safe withdrawal under expert care.
Choosing between residential or outpatient treatment depends on the severity of dependence and lifestyle needs, each offering therapeutic modalities like cognitive behavioral therapy and mindfulness training to foster emotional resilience and behavioral change. Through this process, the individual transitions from instability to recovery, supported by tailored strategies that address both the biological and psychological dimensions of addiction.
A comprehensive scientific review published in 2020 by Keith Humphreys, PhD, and collaborators from Stanford School of Medicine, titled “Alcoholics Anonymous most effective path to alcohol abstinence” in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Review, analyzed 35 studies involving over 10,000 participants and found that Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) was consistently more effective than psychotherapy in helping individuals achieve long-term sobriety.
The review concluded that AA not only improved abstinence rates but also significantly reduced healthcare costs, with one study showing savings of $10,000 per person. The researchers emphasized that AA’s success stems from its strong social support structure, which fosters behavioral change and emotional resilience over time.
What Are the 7 Stages of Sobriety?
There are 7 stages of sobriety which begins with resistance and denial, then progress through acknowledgment, preparation, and action, where individuals face detox and therapy, and move toward maintenance, rebuilding, and finally integrating sobriety into one’s identity. Initial withdrawal symptoms are often the most intense, but they’re temporary with proper medical and emotional support. Recovery spans 12 to 18 months, emphasizing routine, peer connection, and relapse prevention as core pillars of sustained healing.
Listed below are the 7 stages of sobriety in detail below.
- Precontemplation: You resist admitting a problem exists, downplaying consequences, and avoiding discussions about change.
- Contemplation: You weigh the pros and cons of sobriety, gathering information, and confronting ambivalence without yet committing to action.
- Preparation: You develop a concrete plan, selecting treatment options, setting goals, and arranging support, to launch your recovery journey.
- Action: You implement new routines and participate in therapy or support groups, replacing harmful behaviors with healthier alternatives.
- Maintenance: You reinforce sober habits through continued practice, vigilance against triggers, and regular check-ins to prevent relapse.
- Relapse: You experience a temporary return to old patterns, which provides critical insight for refining your strategies and strengthening resolve.
- Termination: You integrate sobriety into your identity and lifestyle so completely that the impulse to return to drinking loses its power.
How Can You Stay Sober?
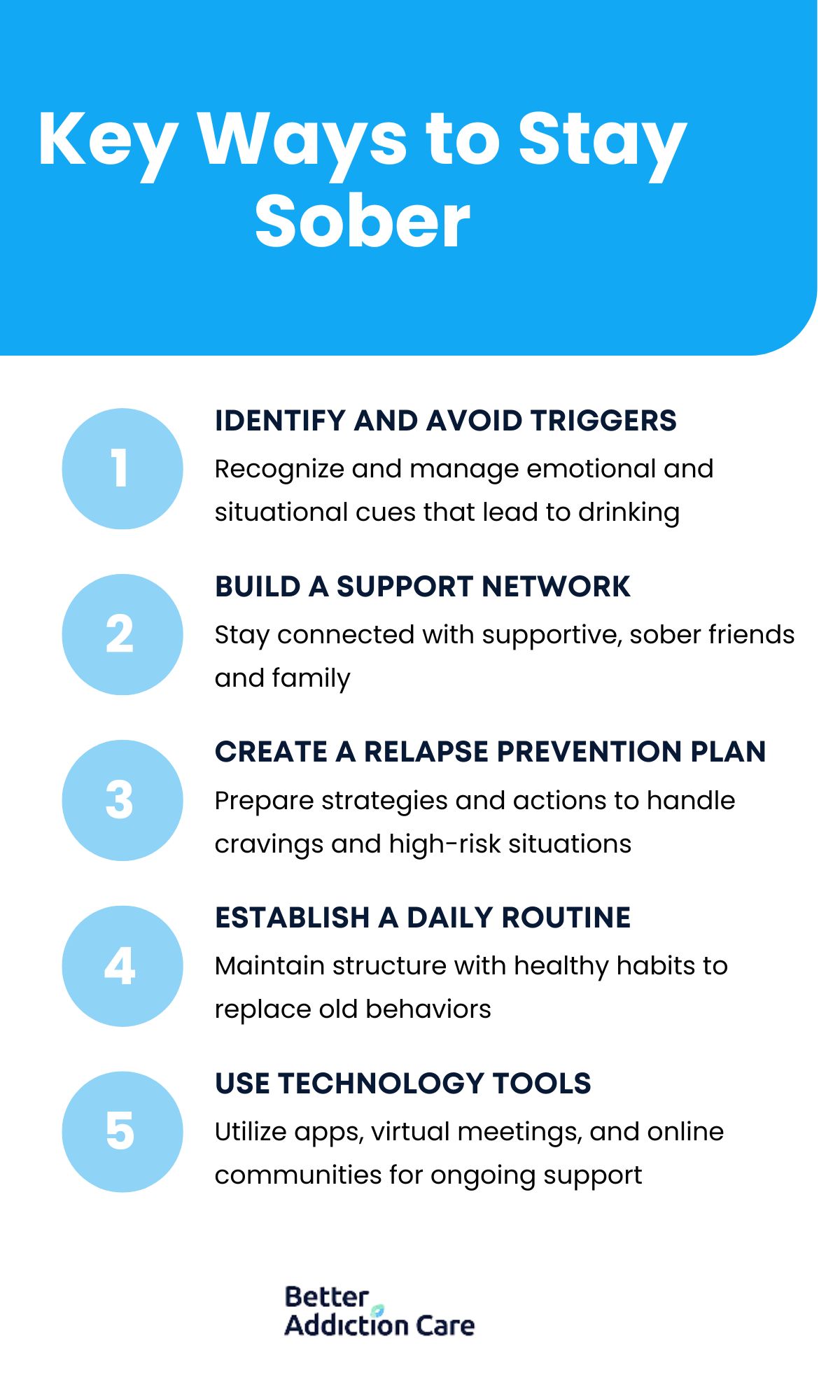
You can stay sober by recognizing triggers, building supportive relationships, creating prevention strategies, maintaining daily routines, and using digital tools. These proven methods work together to strengthen your recovery foundation.
Listed below are 5 ways to stay sober.
-
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers: You stay sober by recognizing specific emotional, environmental, and social cues that provoke drinking urges. Keeping a journal of high-risk situations reveals patterns, while mindfulness breaks automatic reactions. Developing a personalized trigger-management plan, listing coping techniques and support contacts prepares you to navigate temptation with confidence.
-
Building a Support Network: As long as you have people in your life who understand and become involved in your recovery process, everything will be all right. A support network is of the utmost importance, so it is imperative to try to connect with your family, friends, and anyone you trust, feel comfortable with, and who won’t encourage you to relapse. Having support and encouragement for sobriety from positive influences make a significant difference in maintaining your sobriety.
-
Creating a Relapse Prevention Plan: You protect your sobriety by outlining step-by-step responses to cravings and high-risk encounters. Your plan includes immediate actions, calling a sponsor, practicing deep-breathing exercises, and attending an emergency meeting. Integrating aftercare options such as sober living placements or outpatient check-ins ensures that additional support is available whenever it becomes necessary.
-
Establishing a Structured Daily Routine: You reinforce sobriety through a consistent daily schedule that replaces old patterns with healthy habits. Morning rituals include exercise or meditation, while mid-day slots for therapy or work foster purposeful engagement. Evening wind-down activities, reading, gentle stretching, or journaling reduce stress and signal your brain that the day concludes on a sober note.
-
Use Technology Tools: You leverage digital resources to support every stage of recovery. Smartphone apps track mood and craving intensity, alerting you to early warning signs. Virtual support meetings and telehealth counseling provide immediate access to guidance when in-person sessions are unavailable. Online forums connect you to a broader community of individuals who share coping strategies and celebrate milestones.
What Are The Key Phases of the Journey to Sobriety?
The key phases of the journey to sobriety include honest self-assessment, medically supervised detox, structured therapy with peer support, and ongoing aftercare planning.
Listed below are the 4 core phases of the journey to sobriety.
-
Recognizing the Need: Honest self‐reflection and assessment by a clinician establish readiness for change.
-
Detoxification & Early Recovery: Medical supervision manages withdrawal and lays a physical foundation for sobriety.
-
Rehabilitation & Therapy: Structured interventions, including individual counseling, group sessions, and peer mentoring address underlying issues and teach relapse prevention.
-
Sustaining Sobriety: Aftercare services, accountability partnerships, and trigger management plans solidify your new habits.

Which Support Systems Are Crucial for Sustaining Recovery?
The support systems crucial for sustaining recovery are listed below.
-
Professional Help: Licensed counselors, recovery coaches, and structured treatment programs guide clinical progress.
-
Community & Peer Support: Twelve-step groups, peer mentoring, and sober social networks offer lived experience and accountability.
-
Family & Loved Ones: Ongoing encouragement, boundary setting, and family therapy repair relationships and reinforce healthy patterns.
What Common Challenges Arise During Recovery and How Are They Addressed?
Common challenges that arise during recovery include intense cravings, emotional stress, and high relapse risk, and they are addressed through targeted interventions. Physical urges respond to mindfulness exercises and breathing techniques that interrupt automatic reactions. Emotional upheaval settles with cognitive reframing and motivational interviewing that reinforce coping skills. Exposure to old social circles loses power when you replace harmful routines with new activities and maintain regular check-ins with sponsors or peer mentors.
How Can Long-Term Sobriety Be Maintained Beyond Initial Treatment?
You maintain long-term sobriety by engaging in structured aftercare and adopting sustainable habits. Aftercare services such as sober living residences, outpatient alcohol rehab, and alumni support groups reinforce coping skills and provide accountability. Celebrating key milestones, regularly updating your relapse-prevention plan, and embracing recovery as a continuous journey, sustain motivation and strengthen resilience.
What Are the 3 P’s of Sobriety?
The 3 P’s of sobriety include patience, perspective, and progress.
Patience requires accepting that meaningful change unfolds over time and resisting the urge for instant results. Embracing a steady pace helps you remain committed during challenging phases.
Perspective involves reframing obstacles as opportunities to refine your approach and deepen insight into recovery, viewing setbacks as lessons that build resilience and strengthen resolve.
Progress focuses on tracking specific milestones, such as 30, 90, and 365 days sober—so you celebrate tangible achievements rather than chasing an impossible ideal. This emphasis on incremental gains sustains motivation.
What Is the Hardest Stage of Sobriety?
The hardest stage of sobriety is the initial withdrawal period, when physical and psychological demands peak. This stage unfolds across three challenging phases:
-
Early Withdrawal (Days 1–7): Physical detox provokes severe discomfort, including sweating, tremors, insomnia, and intense cravings that require medical oversight and disciplined coping tactics.
-
Psychological Adjustment (Weeks 1–3): Mood swings, anxiety, and emotional volatility emerge as your brain recalibrates, demanding regular therapy and mindfulness practices to navigate triggers.
-
Long-Term Maintenance (Months +): Sustaining motivation over time and continuously updating relapse-prevention strategies prove critical to avoid complacency and reinforce resilience.
How Long Does the Path to Sobriety Take?
The path to sobriety typically spans 12 to 18 months for meaningful, sustained recovery. This includes 7–10 days for detox, 30 to 90 days of structured treatment, and ongoing aftercare and lifestyle changes for the remainder of the year and beyond.
Why Is Peer Support Crucial?
Peer support is crucial because it provides real-time empathy, accountability, and encouragement from those who understand the recovery process. Group meetings and sponsor relationships reduce isolation and build confidence in long-term sobriety.
How Does Relapse Prevention Work?
Relapse prevention works by identifying personal triggers, practicing coping strategies, and using support systems like sponsors or emergency groups, before high-risk moments escalate.
Where Can One Find Aftercare Services?
You can find aftercare services through rehab referrals, sober living programs, alumni networks, local recovery groups, and online directories that connect you to long-term support.
How to Find a Local Alcohol Rehab Center Near Me?
To find a local drug and alcohol rehab center near you, start by speaking with a medical professional or contacting a treatment helpline for immediate guidance. Use reputable directories or verified online platforms to locate licensed facilities that match your recovery needs, whether inpatient, outpatient, or detox programs.
At Better Addiction Care, we provide a trusted local alcohol rehab facility locator to simplify your search. Our network connects you with accredited providers offering personalized treatment options, ensuring your path to recovery begins with the right support.







