Better Addiction Care Blogs


Mental Health Awareness Month is a nationwide observance dedicated to raising awareness surrounding mental health. From anxiety and depression to trauma and co-occurring disorders, Mental Health Awareness Month highlights the broad range of challenges people face and emphasizes that mental health is just as important as physical health.

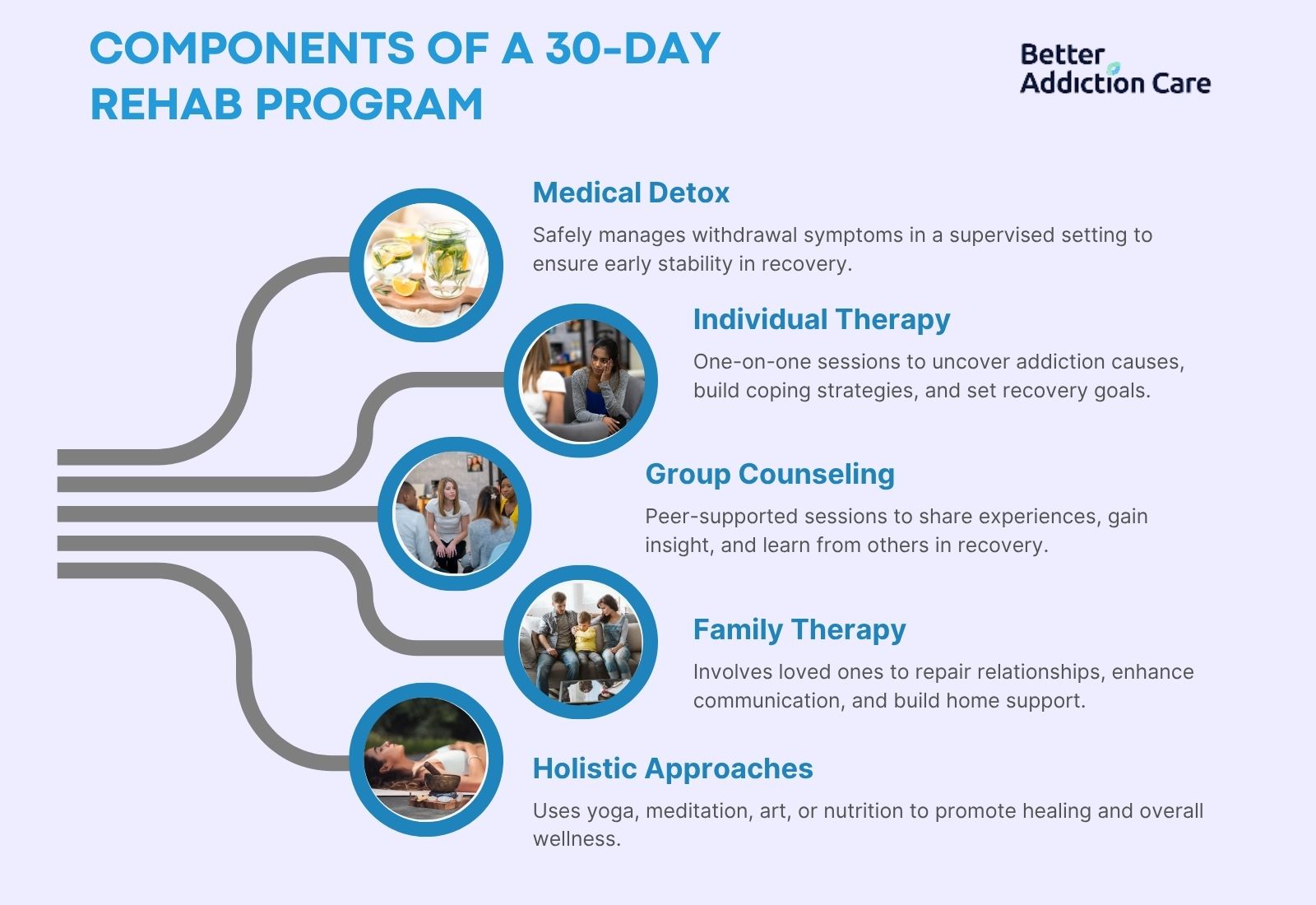
Mental health therapy is a structured treatment approach designed to help individuals manage and overcome psychological and emotional challenges. Therapy is important for addressing mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, PTSD, and substance use disorders, providing individuals with the tools they need to lead healthier and more fulfilling lives.

Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) focuses on identifying and modifying the thought patterns and behaviors that lead to and sustain addictive behavior. It emphasizes active participation, practical skill development, and consistent practice through a structured form of therapy led by trained therapists.

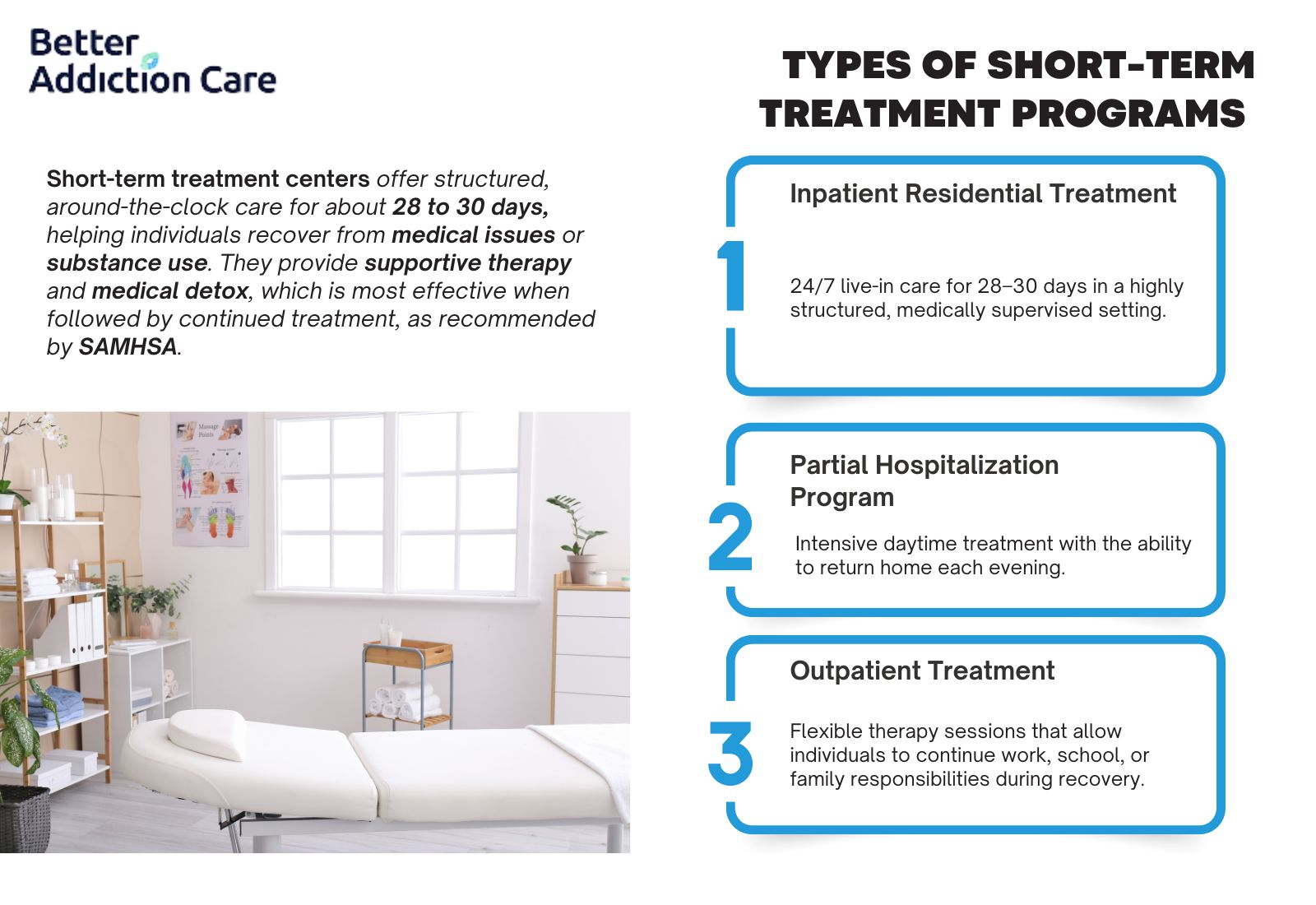
Partial Hospitalization Programs (PHP) provide structured therapy, medical supervision, and relapse prevention while allowing individuals to live at home. According to a study by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) 2022, individuals in PHPs have a 54% higher treatment retention rate compared to those in standard outpatient programs.

A halfway house is a structured, substance-free living environment designed to support individuals transitioning from treatment to independent, sober living. These residences serve as a bridge between intensive addiction treatment and full reintegration into society, offering stability, accountability, and continued recovery support.

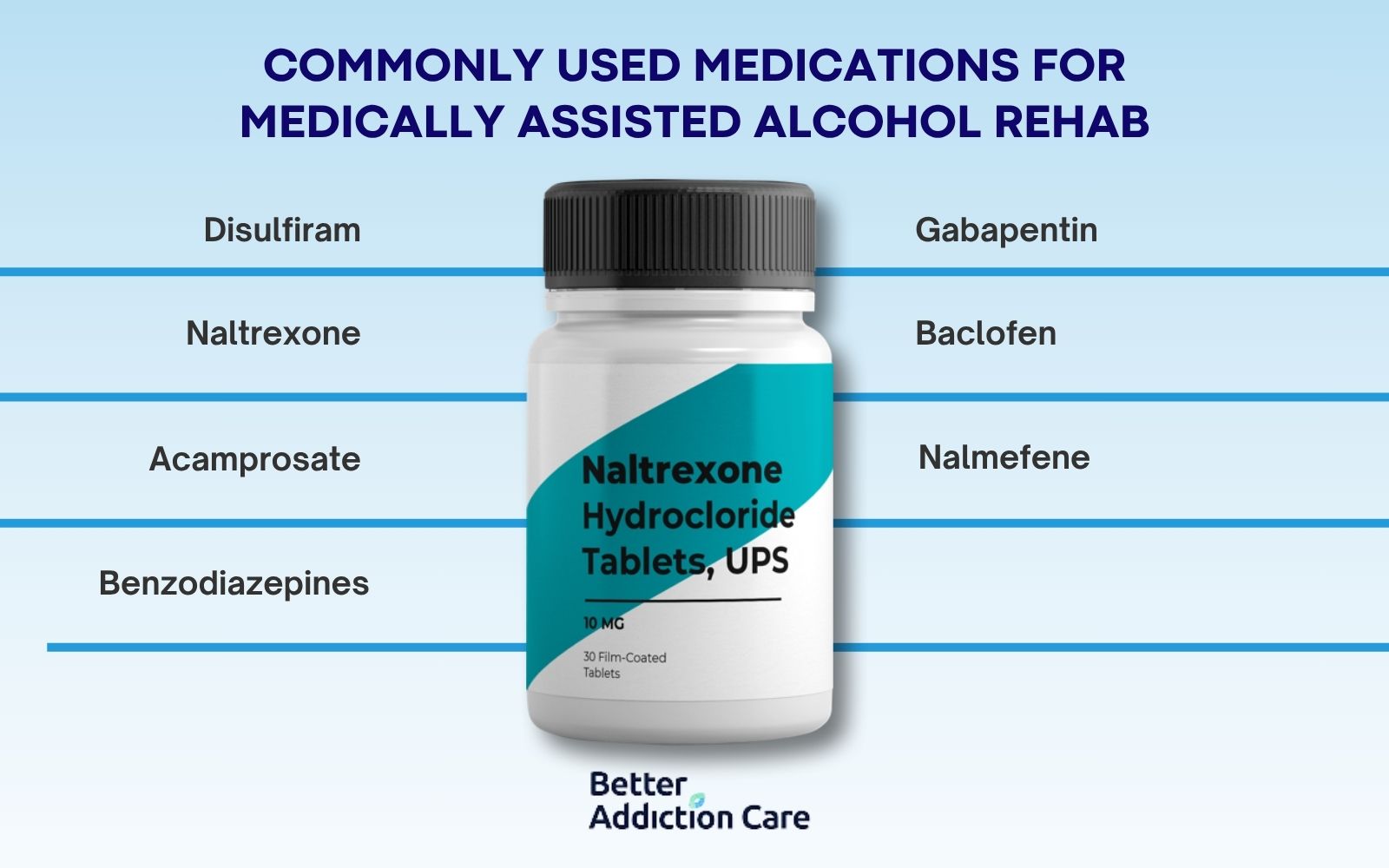


Alcohol addiction, also known as alcoholism, is a chronic disease where individuals lose control over their drinking habits despite harmful consequences. Alcohol use disorder is marked by both physical and psychological dependence, which causes significant damage to one’s health and life over time.


Psychiatric rehabilitation helps individuals with severe mental health conditions regain independence, develop coping skills, and reintegrate into society. Psychiatric rehabilitation focuses on improving emotional, social, and vocational functioning through structured interventions, combining therapy, medication management, and life skills training to enhance overall well-being.
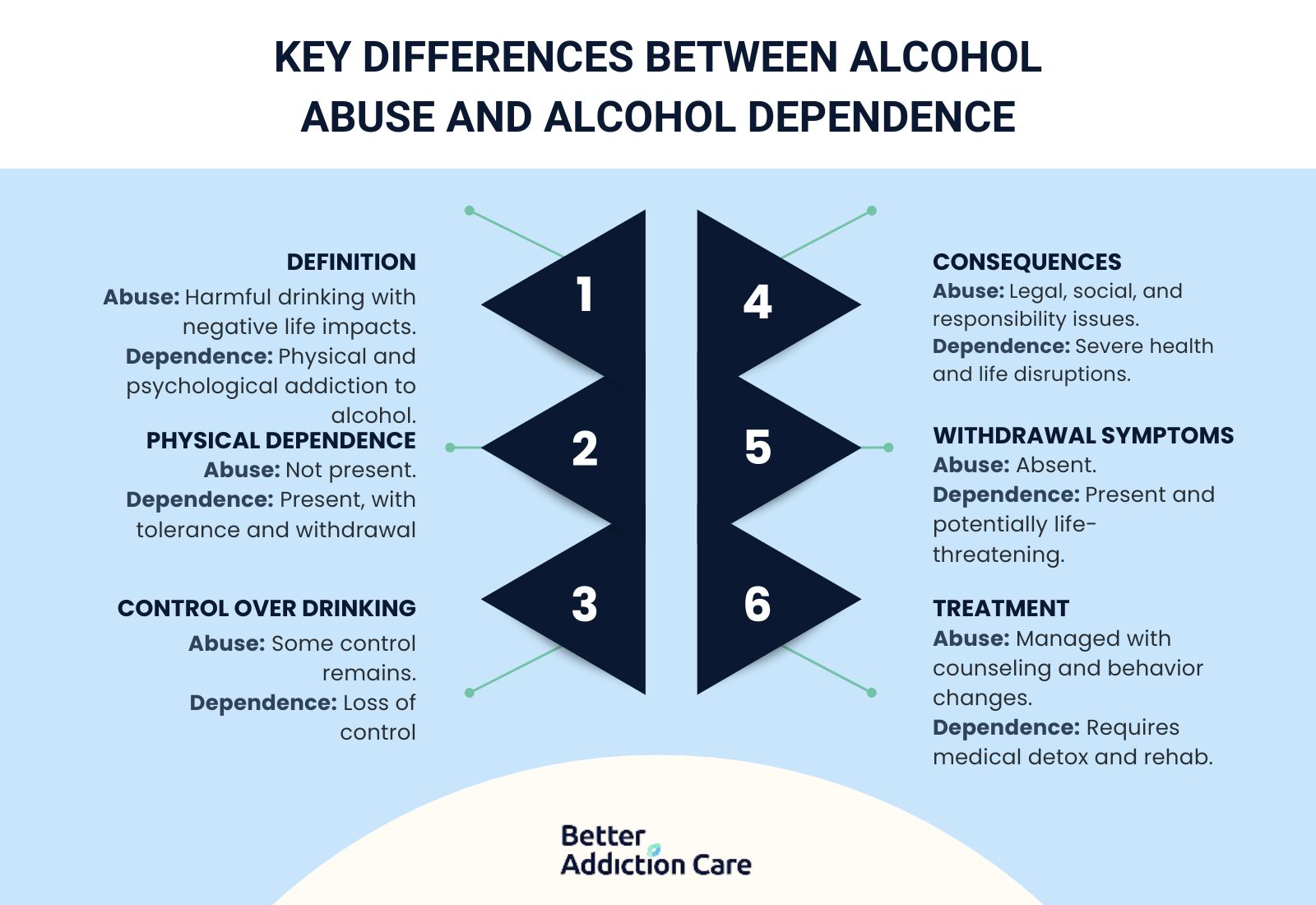
dependence states that abuse involves harmful drinking patterns without full physical reliance, while dependence includes tolerance and withdrawal, with causes rooted in social, psychological, and biological factors, and rehabilitation requiring counseling, medical treatment, and long-term support.

Mixing Lunesta and alcohol is highly dangerous because it intensifies central nervous system depression, increases mental instability, and significantly raises the risk of fatal overdose.Mixing Lunesta (eszopiclone) and alcohol creates a dangerous combination that significantly impacts the central nervous system.